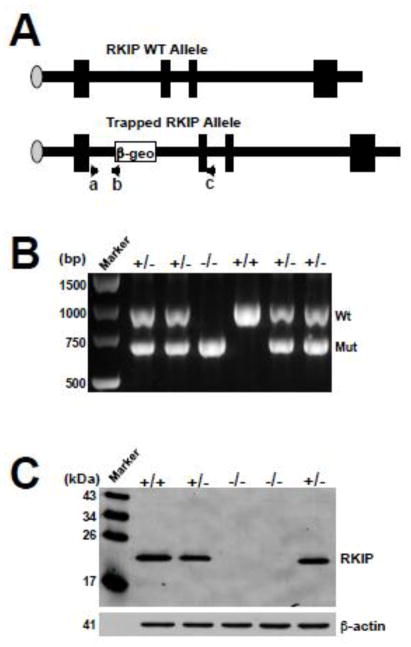
Figure 1. Knockout (KO) of the RKIP gene in mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the genomic structure of wild type RKIP and the trapped RKIP allele. The PCR primers for genotyping were indicated as a, b, and c. Primers a + b produce approximately 600 bp PCR fragments for detecting the RKIP gene trapped allele, and primers a + c produce 978 bp PCR fragments for detecting the RKIP wild-type allele. (B) PCR genotyping of offspring from a RKIP+/− intercross. The 978 bp product corresponds to the wild-type allele (Wt) and the 600 bp product corresponds to the mutant allele (Mut). (C) Western blot analysis with the anti-RKIP antibody of whole-cell protein lysates from E12.5 embryos derived from a RKIP+/− intercross.