Figure 8. Proposed mechanism for the increased susceptibility of NKT cell deficient mice to APAP-induced liver injury.
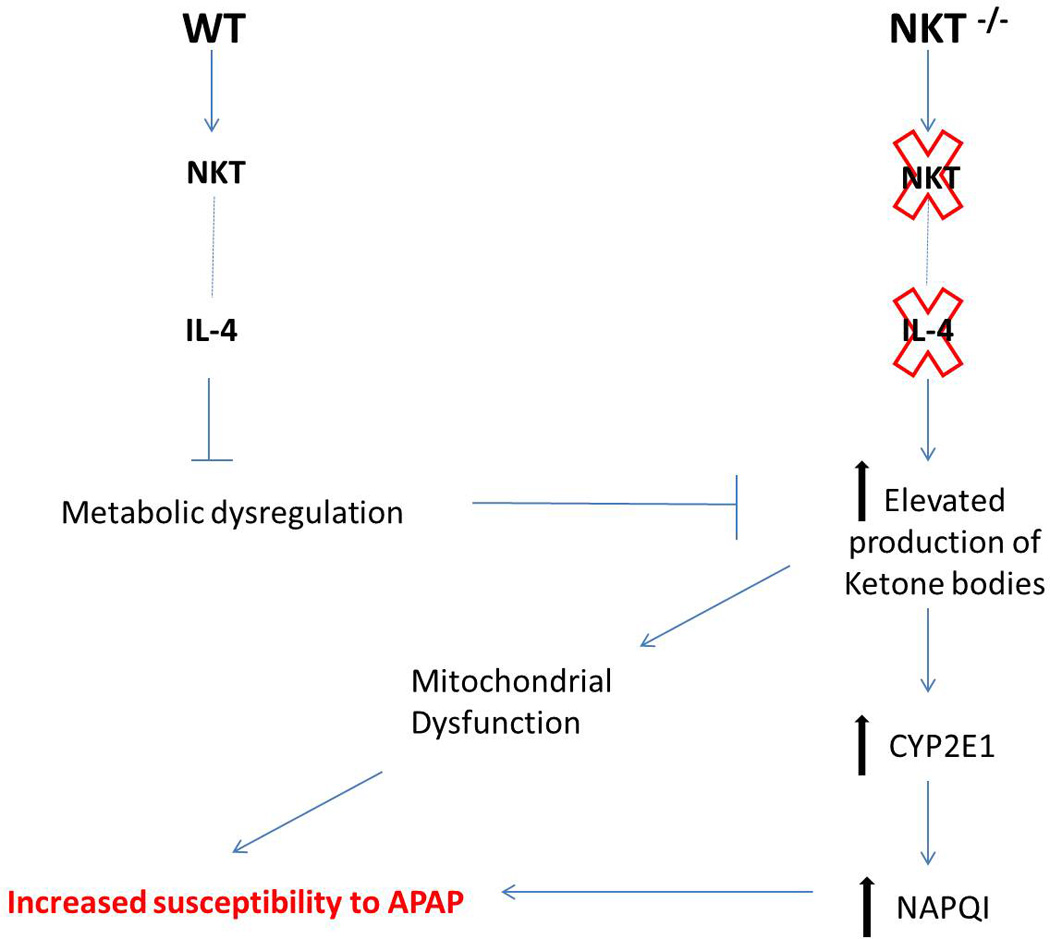
We hypothesize that the intrinsic IL-4 production by NKT cells may be critical in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Thus, inhibiting the elevation of ketone bodies that are known modulators of CYP2E1 stability. Elevated CYP2E1 can lead to elevated NAPQI metabolite and overall increased susceptibility to AILI.
