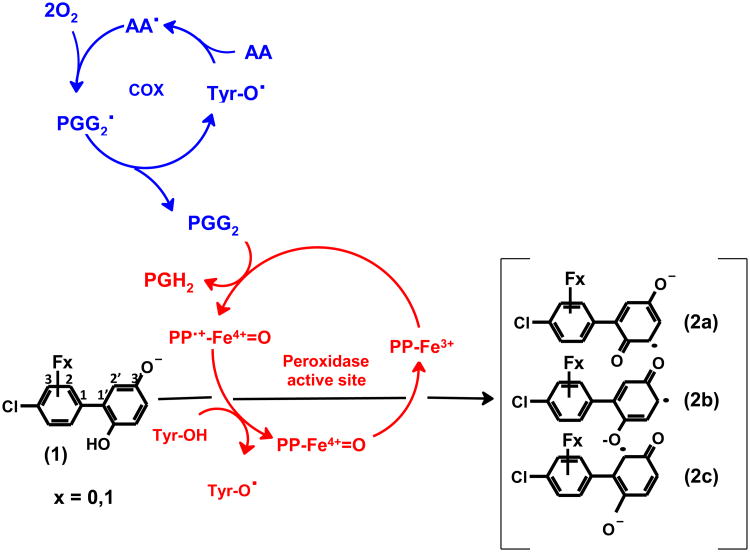
Figure 1.
Oxidation of 4-chlorobiphenyl-2′,5′-hydroquinone (1) or its fluoro-substituted analogues (2-fluoro-4-chlorobiphenyl-2′,5′-benzoquinone or 3-fluoro-4-chlorobiphenyl-2′,5′-benzoquinone), to mesomeric 4-chlorobiphenyl-2′,5′-semiquinones (2a-c) as catalyzed by PGHS. Tyr384 residue (Tyr-OH) in the cyclooxygenase active site is activated by a one-electron oxidation by the ferryl-oxo protoporphyrin radical (PP•π-Fe=O) at the active site of the peroxidase. The resulting tyrosyl radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from arachidonic acid (AA) to create a carbon-centered radial, AA•. This radical leads to reactions that consume two molecules of dioxygen producing prostaglandin G2 (PGG2). PGG2 is reduced to prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) by the peroxidase activity.