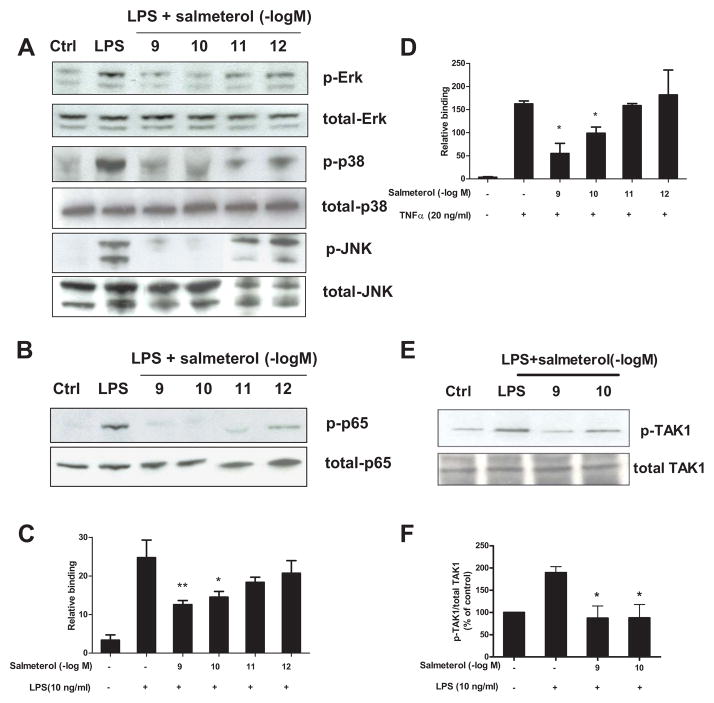
FIGURE 8.
Salmeterol significantly suppresses LPS-induced MAPK and NF-κB activation through inhibition of TAK-1 phosphorylation. Enriched microglia were pretreated with vehicle or salmeterol (10−9–10−12 M) for 30 min followed by treatment with LPS (10 ng/ml) for 15 min. Cells were then harvested, and the amounts of phosphorylated and total MAPK (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK1/2) (A) and phosphorylated and total NF-κB p65 (B) were determined by western blot analysis, respectively. Representative western blots for ERK1/2, p38, JNK and p65 phosphorylation are shown from 3 independent experiments. Figures C and D: primary microglia were pretreated with salmeterol (10−9–10−12 M) for 30 min, then treated with LPS (C) or TNFα (D) for 30 min. Nuclear extracts were prepared from these cells, and NF-κB (p65) DNA binding activity was detected using the NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay Kit. Figure E and F: Enriched microglia were pretreated with vehicle or salmeterol (10−9–10−10 M) for 30 min followed by the treatment with LPS (10 ng/ml) for 15 min, cells were then harvested, and the amounts of phosphorylated TAK1 and total TAK1 are show in western blot analysis using specific antibodies (E). ImageJ software was used to quantitate the intensity of the phosphorylated TAK1 and total TAK1 bands in western blot, and the results given in figure F represents the percentage difference of the ratio of phosphorylated TAK1 compared with total TAK1 normalized to the vehicle-treated control (F).