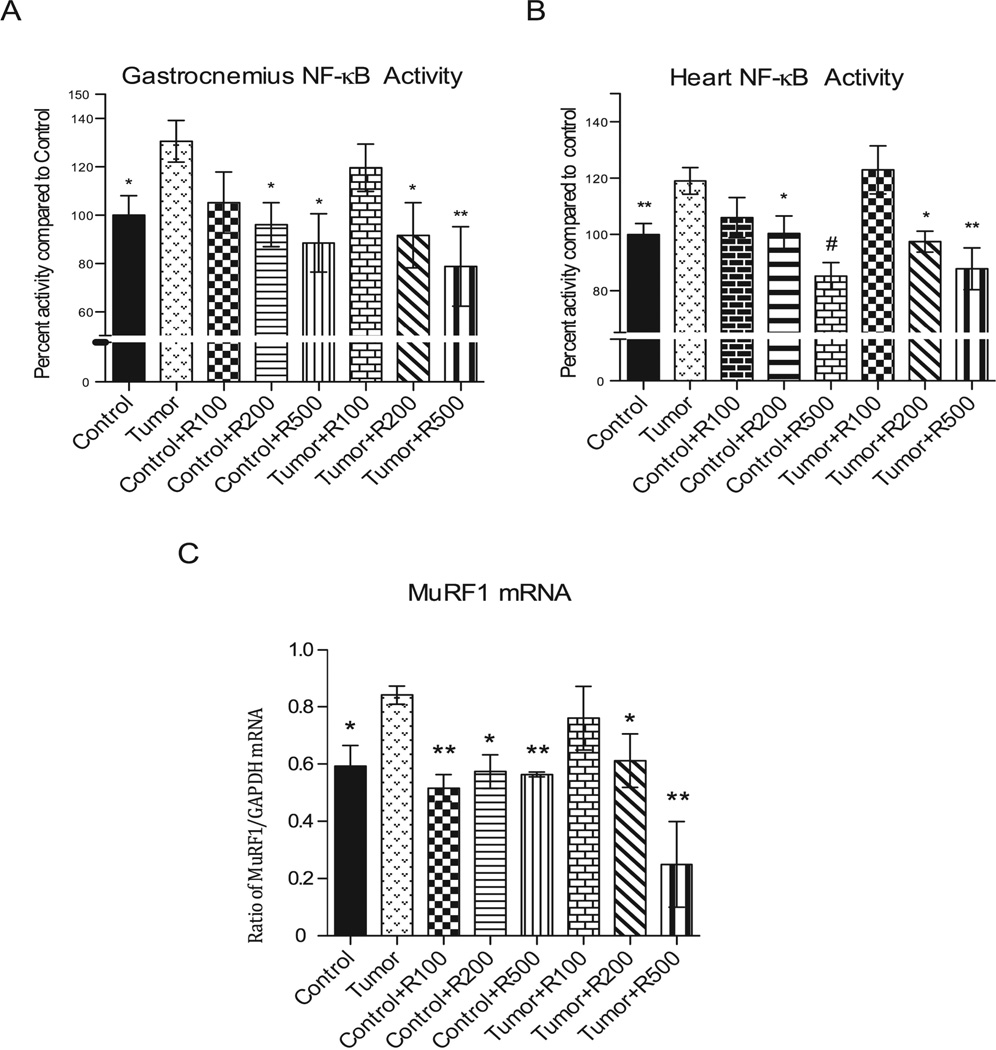
Figure 5. Nuclear factor-kappa B activity (p65).
(A) Nuclear extractions on gastrocnemius muscle were analyzed looking at p65 bound DNA activity. Significant increase in activity was noted in untreated tumor bearing mice compared to control. Tumor bearing mice treated with resveratrol showed a significant decrease in NF-κB activity at 200 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg dosages. Also of note in the treated non-tumor bearing group NF-κB activity was significantly decreased and comparable to control with administration of resveratrol at the 200 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg dosages. (B) The tumor bearing groups receiving 200 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg resveratrol showed significant inhibition of tumor-induced NF-κB activity. (C) Tumor bearing mice receiving 200 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg resveratrol had an inhibition of tumor-induced MuRF1 expression. mRNA expression was measured and depicted here as normalized to GAPDH controls. # = p <0.001, ** = p < 0.01, * = p < 0.05. For (A) and (B): N=12 (Control); N=4 (Control + R100), N=4 (Control + R200), N=4 (Control + R500), N=4 (Tumor), N=4 (Tumor +R200), N=4 (Tumor + R500). For (C): N=4 (Control), N=3 (Control + R100), N=3 (Control + R200), N=3 (Control + R500), N=4 (Tumor), N=3 (Tumor +R100), N=3 (Control + R200), N=3 (Control +R500).