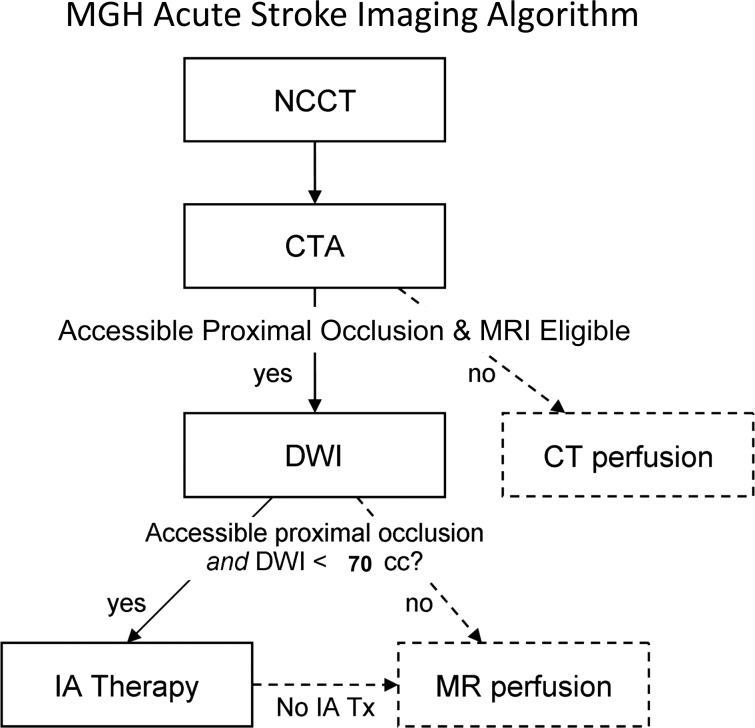
Figure 4.
Massachusetts General Hospital acute stroke imaging algorithm for triage of patients with severe ischemic strokes caused by anterior circulation occlusions. All patients undergo non-contrast CT (NCCT) followed by CT angiography (CTA). If the patient has severe neurological deficits (National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score ≥10), no large hypodensity and no hemorrhage on NCCT, and an occlusion is identified of the distal internal carotid artery and/or proximal middle cerebral artery that is accessible by microcatheter, then the patient is immediately evaluated by diffusion MRI if there are no contraindications to MRI. If the diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) lesion is small, defined as <70 ml, then the patient is immediately triaged to endovascular therapy if the patient is otherwise eligible for such treatment. If the patient is not eligible for MRI, he/she may undergo a CT perfusion study for possible guidance for therapy or for prognostic information. Also, if the patient is not eligible for endovascular therapy, CT or MR perfusion may be performed for similar reasons. Only the first step in this algorithm (NCCT) and the time from stroke onset are needed for the decision to treat with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. IA, intra-arterial.