Figure 5.
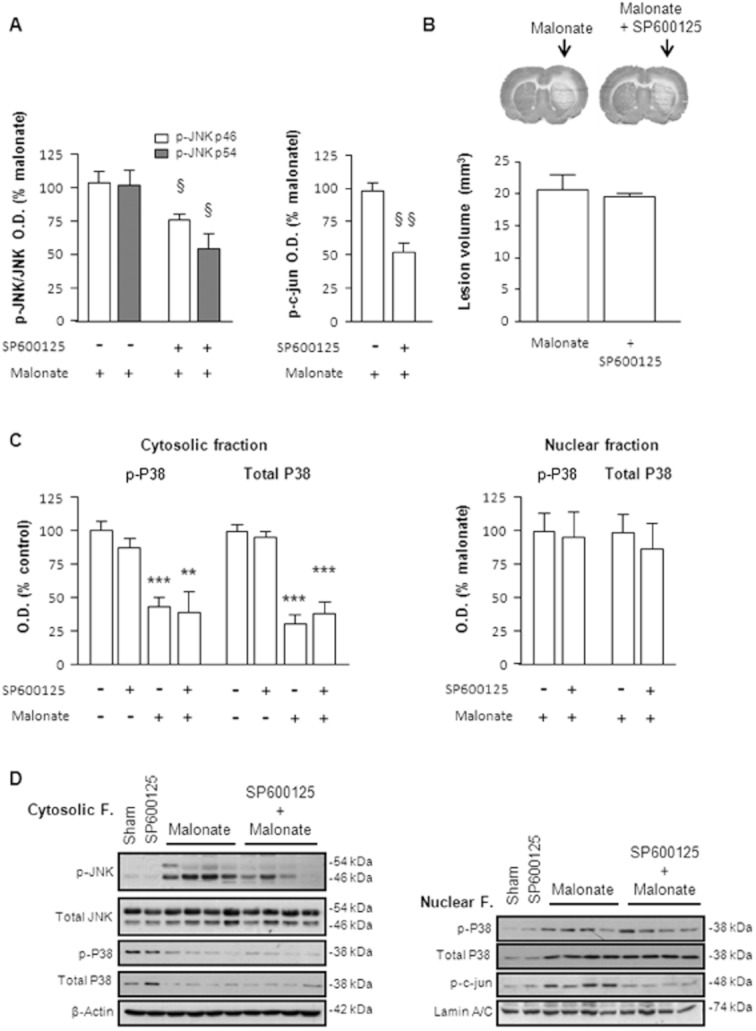
Effect of the JNK inhibitor, SP600125, on malonate induced neurotoxicity. SP600125 (1 nmol/2 μL) was administered intrastriatally in combination with malonate (1.5 μmol/2 μL). (A) Quantitative measurement of optical density showing that SP600125 produced a half/significant decrease in JNK and c-jun phosphorylation caused by malonate. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5–8). Data analysed by Student's t-test revealed significant differences: for p-JNK 46 kDa [t(8) = 2.565, P < 0.05], for p-JNK 54 kDa [t(9) = 2.721, P < 0.05] and for p-c-jun [t(10) = 4.544, P < 0.05]. (B) Representative cytochrome oxidase-stained slices and quantification of malonate-induced striatal lesions (mm3) show that SP600125 failed to inhibit the neurotoxic effect of malonate observed 72 h after treatment. (C) SP600125 had no effect on p38 translocation to the nucleus. (D) Representative blots from nuclear and cytosolic fractions showing the effects of SP600125 on malonate-induced activation of the SAPKs pathway 6 h after treatment.
