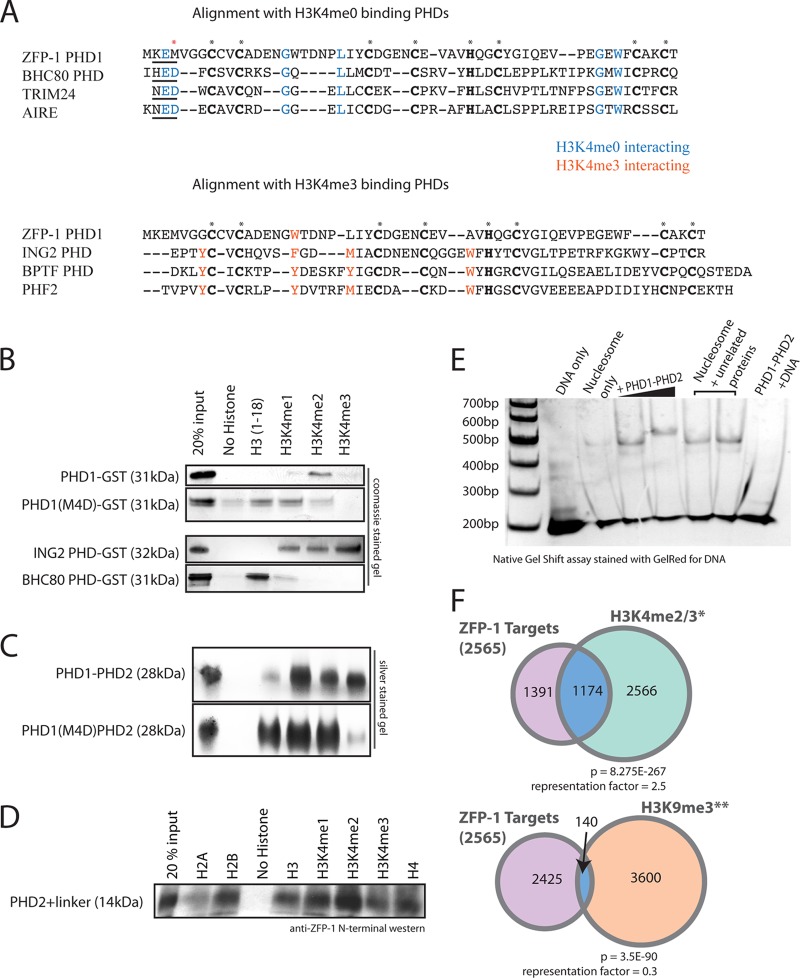
Fig 9.
PHD1-PHD2 domain interacts with nucleosomes, and its PHD1 zinc finger shows specificity for methylated H3K4. (A) Primary sequence alignment of ZFP-1 PHD1 with various PHD fingers. The top panel shows an alignment with PHD fingers known to bind H3K4me0, with residues that interact with the lysine side chain highlighted in blue. The bottom panel shows ZFP-1 PHD1 aligned with PHD fingers known to interact with H3K4me3, with residues known to form an aromatic cage around H3K4me3 highlighted in orange. Conserved cysteine and histidine residues that represent the PHD finger domain are highlighted in bold and indicated with asterisks. The red asterisk indicates methionine 4, investigated as described below. (B) In vitro binding assays of GST-fused PHD fingers with biotinylated histone H3 tails, as indicated. PHD1-GST specifically bound H3K4me2 but lost specificity for this mark when methionine 4 was mutated to aspartic acid (M4D). BHC80 PHD-GST bound unmethylated H3K4 and ING2 PHD-GST bound methylated H3K4, consistent with previous findings (19, 32, 34), as shown by Coomassie blue staining after SDS-PAGE. (C) (Top) PHD1-PHD2 binds all states of methylated H3K4 but not the unmethylated H3 tail. (Bottom) PHD1-PHD2 with M4D mutation loses specificity for H3K4me3 and shows affinity for the unmethylated H3 tail. Silver-stained SDS-PAGE gels are shown. (D) PHD2+linker binds all histone tails nonspecifically. (E) PHD1-PHD2 binds to nucleosomes in vitro. A GelRed-stained native gel containing nucleosomes incubated with increasing concentrations of PHD1-PHD2 is shown. DNA only, 200-bp sequence used to reconstitute the nucleosomes from histone octamers; nucleosome only, band corresponding to a nucleosome monomer (24). Increasing concentrations of PHD1-PHD2 led to a gel shift showing an interaction between PHD1-PHD2 and the nucleosome monomer. A control incubation of PHD1-PHD2 with DNA is shown in the rightmost lane. (F) Venn diagrams showing overlap of previously described ZFP-1 ChIP-chip targets (22) with H3K4me2/3 peaks (38) or H3K9me3 peaks (52). A total of 1,174 of 2,565 ZFP-1-bound genomic regions also had H3K4me2/3 peaks, which represents a significant enrichment (top); however, only 140 of 2,565 ZFP-1 targets also had H3K9me3, representing a significant depletion.