Fig 1.
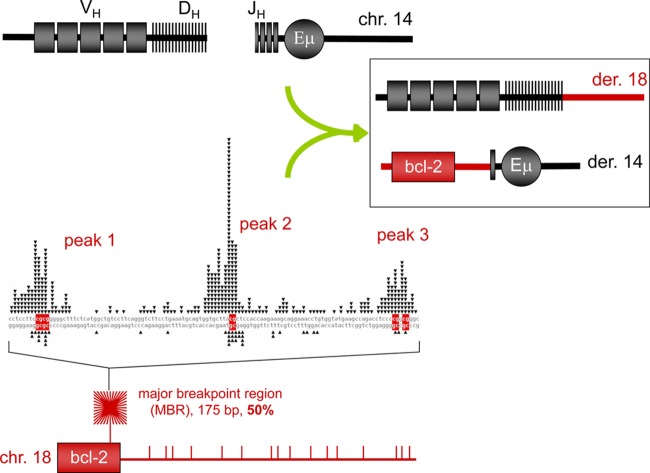
Diagram of bcl-2 translocation. The bcl-2 translocations occur between the IgH locus on chromosome 14, mostly during DH-to-JH recombination, and the bcl-2 locus on chromosome 18, mostly downstream of the coding portion of the bcl-2 gene. About 50% of patient translocation breaks occur within the 175-bp major breakpoint region (MBR), which is shown as the red starburst square at the bottom left and expanded to a sequence level above it. The MBR breakpoint distribution from follicular lymphoma patients show highly significant focusing on three CpG peaks (see DNA sequence in the middle left of figure). The side of the break closest to the bcl-2 gene (telomeric side) joins to the JH segment of IgH locus on chromosome 14 and becomes the derivative 14 (der 14). The centromeric side of the bcl-2 locus usually joins to the DH segment and becomes derivative 18 (der 18). In the DNA sequence of the MBR (middle left), the triangles on top of the sequence represent the breakpoints sequenced from the derivative chromosome 14, and the triangles on the bottom of the sequence represent breakpoints sequenced from the derivative chromosome 18. The bottom panel shows the approximate distribution propensity of translocation breakpoints occurring around the MBR region of the bcl-2 gene on chromosome 18 in human patients. The density of lines in the starburst square represents the number of breakpoints at the MBR region relative to breakpoint outside of the MBR region (shown as the vertical bars to the right of the starburst).