Fig 2.
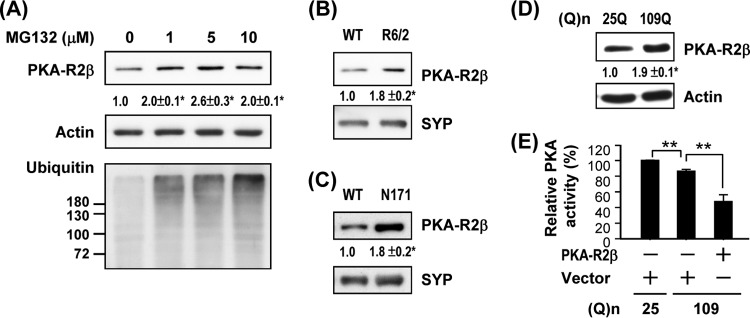
Impairment of proteasome activity caused accumulation of PKA regulatory subunits and suppression of PKA activity. (A) ST14A cells were treated with vehicle or MG132 for 6 h. Lysates collected for the indicated condition were used to determine the expression of PKA-R2β by a Western blot analysis. Data points represent the means ± SEM for three independent experiments. Synaptic fractions of the striatum of 12-week-old R6/2 mice and littermate controls (B) or 16-week-old N171-82Q mice and littermate controls (C) were used to determine the expression of PKA-R2β by a Western blot analysis. (D) ST14A cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-Htt-(Q)25-hrGFP or pcDNA3.1-Htt-(Q)109-hrGFP for 72 h. Lysates collected for the indicated condition were used to determine the expression of PKA-R2β by a Western blot analysis. (E) ST14A cells were cotransfected with pcDNA3.1-Htt-(Q)25-hrGFP or pcDNA3.1-Htt-(Q)109-hrGFP and pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-PKAR2β for 72 h. Lysate collected for the indicated condition was used to determine PKA activity. Data are presented as the means ± SEM for 3 experiments. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01 (by one-way ANOVA).
