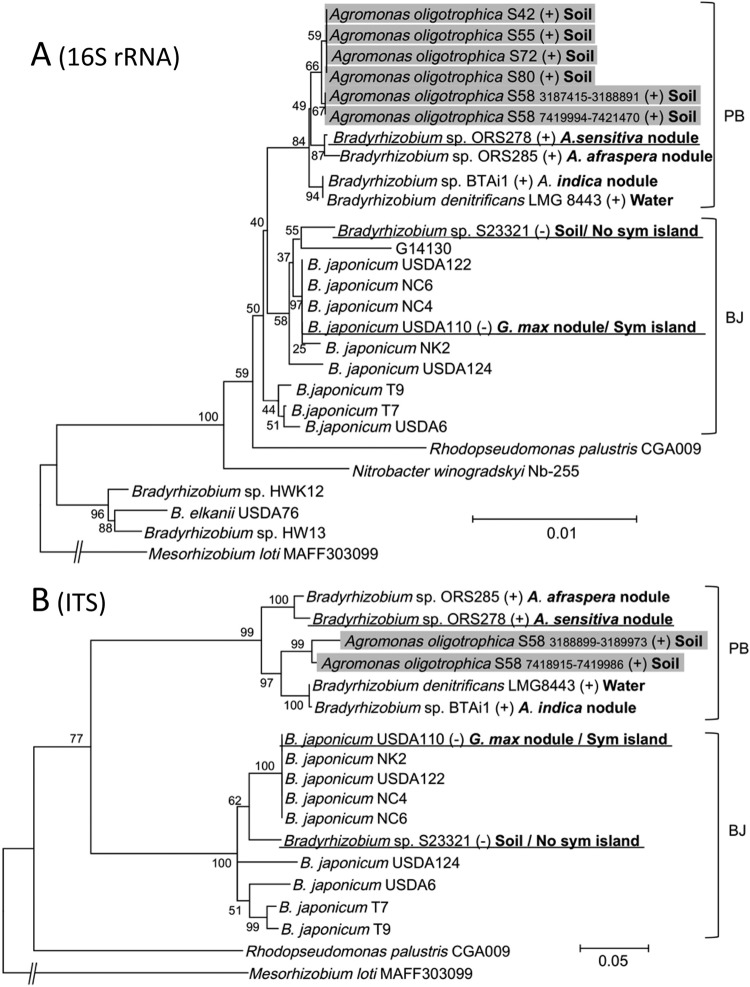
Fig 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of Agromonas oligotrophica S58 and other members of the Bradyrhizobiaceae determined on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequences (A) and internal transcribed spacer sequences (B). For all trees, Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099 was used as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes are the percentages of 1,000 bootstrap replications supporting that partition. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% of the bootstrap replicates are not shown. Isolation sources are shown following strain names. Positive and negative data representing Nod factor-independent nodulation on A. indica are marked with (+) and (−), respectively. Bradyrhizobium sp. S23321 isolates from soil lacked symbiosis (sym) island-containing nodABC genes and do not nodulate soybean (Glycine max) and sitratro (13), whereas B. japonicum USDA110 with symbiosis islands nodulates soybean and siratro in a Nod factor-dependent manner (13, 31). Abbreviations: PB, photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium clade; BJ, Bradyrhizobium japonicum clade. Although both soil-dwelling A. oligotrophica S58 (PB) and Bradyrhizobium sp. S23321 (BJ) lacked symbiosis islands, S58 (PB) exclusively nodulates A. indica in a NF-independent manner.