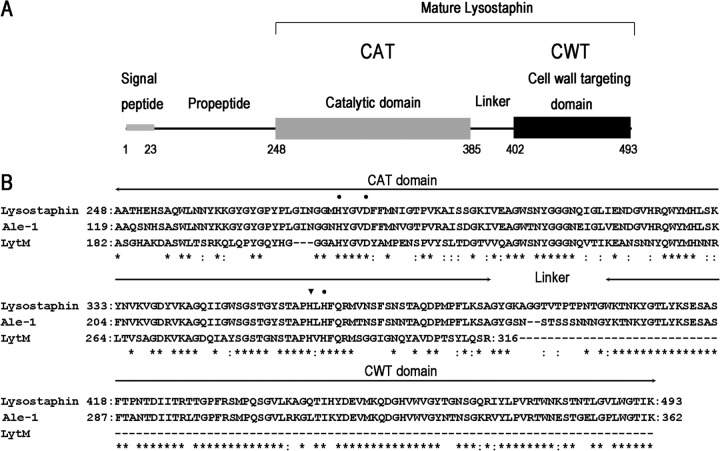
Fig 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain architecture of preprolysostaphin. Lysostaphin is expressed in Staphylococcus simulans as a 493-aa preproenzyme (UniProt entry P10547) and secreted via the signal peptide. Removal of the propeptide during secretion by an extra cysteine protease generates the 246-aa mature lysostaphin, which consists of an N-terminal catalytic domain (CAT), a C-terminal bacterial cell wall targeting domain (CWT), and a short linker in the middle. The CAT domain is a zinc-containing metalloprotease that cleaves glycylglycine bonds in the pentaglycine cross bridges of S. aureus. The CWT domain belongs to the SH3b family, which is necessary for accurate cell wall recognition. The CWT domain directs the CAT domain to its substrates on the surface of S. aureus. (B) Sequence alignment of lysostaphin to ALE-1 and LytM using BLAST. ALE-1 is a staphylolytic enzyme produced by S. capitis EPK1. ALE-1 (residues 119 to 362) and lysostaphin (residues 248 to 493) share 83% sequence identity and 88% similarity. LytM is an autolysin from S. aureus. The CAT domains of LytM (residues 182 to 316) and lysostaphin (residues 248 to 384) share 48% sequence identity and 63% similarity. Amino acid residues conserved in these proteins are indicated by asterisks; conserved substitutions are indicated by colons. Zinc binding sites and the active site of the CAT domain are indicated by dots and an inverted triangle, respectively.