Fig 5.
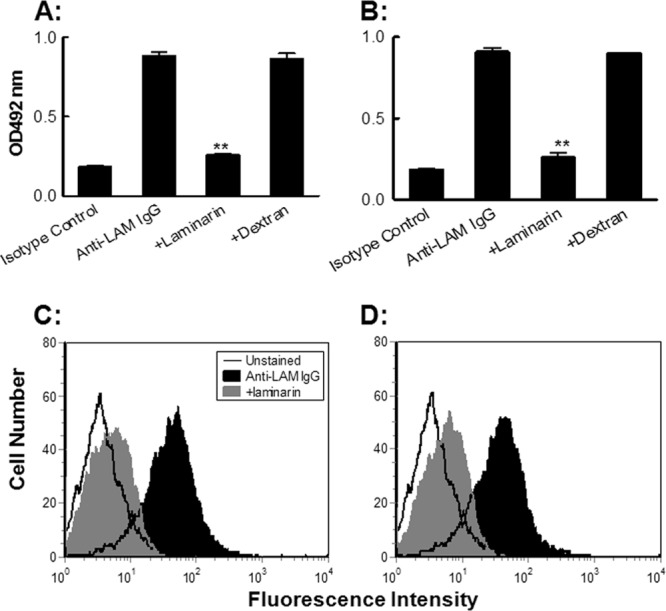
Recognition of yeast particles by IgG Abs induced by LAM-CRT vaccination. (A and B) Laminarin-specific IgG Abs (20 μg/ml), affinity purified from LAM-CRT-induced antisera of BALB/c (A) or nude (B) mice by using a laminarin-conjugated Sepharose 6B column and then a protein A/G-agarose column, were tested for the ability to bind viable C. albicans particles precoated onto ELISA plates, and HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG was employed as a detection Ab; the results are expressed as the mean OD492 ± SD of triplicate wells. For competition inhibition, the affinity-purified IgG Abs were incubated with either laminarin or dextran (100 μg/ml) at 37°C for 1 h and then dispensed in ELISAs. **, P < 0.01. The affinity-purified IgG Abs from BALB/c (C) and nude (D) mice were further analyzed for the ability to bind C. albicans by flow cytometry. Heat-killed C. albicans cells (2 × 106 particles) were sequentially treated with affinity-purified Abs (filled dark histograms, 20 μg/ml) or left untreated (open histogram) and then treated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled anti-mouse IgG followed by analysis using a BD FACSCalibur flow cytometer. The yeast cells were also stained with affinity-purified Abs preincubated with laminarin (100 μg/ml) at 37°C for 1 h (filled gray histogram) as an additional specificity control. Data represent the results from at least three independent experiments.
