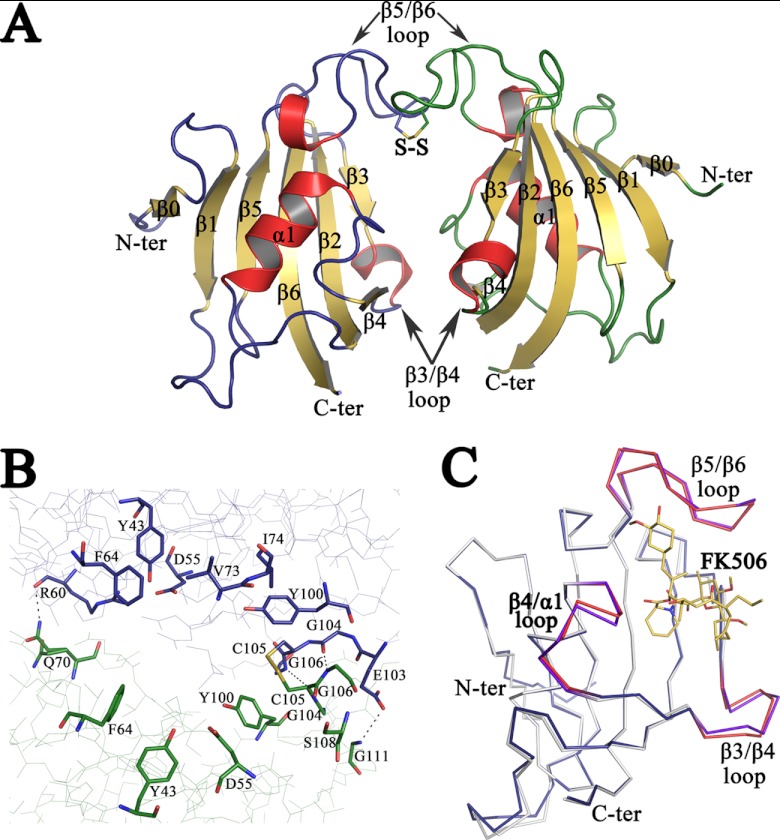
Fig 1.
Crystal structure of apo PvFKBD35. (A) The overall structure of the FKBD35 domain of P. vivax is shown as a cartoon diagram. The disulfide bond between Cys 105 of both chains is displayed in stick mode with the sulfur atoms colored in yellow. The loops corresponding to chains A (left) and B (right) are colored blue and green, respectively, while the helices are colored red and sheets are in yellow. (B) Close view of active-site residues, in stick mode, that line up the dimer interface formed between the two PvFKBD35 (chain A, blue; and chain B, green) molecules in the asymmetric unit. The disulfide bond is shown as a stick, and hydrogen bonds are displayed as dashed lines. (C) Shown is the superimposition of the backbone traces of apo PvFKBD35 colored in blue (β3-β4, β4-α1, and β5-β6 loops colored red) and FK506-bound PvFKBD35 colored in white (β3-β4, β4-α1, and β5-β6 loops colored purple). The FK506 inhibitor is shown as yellow-colored sticks.