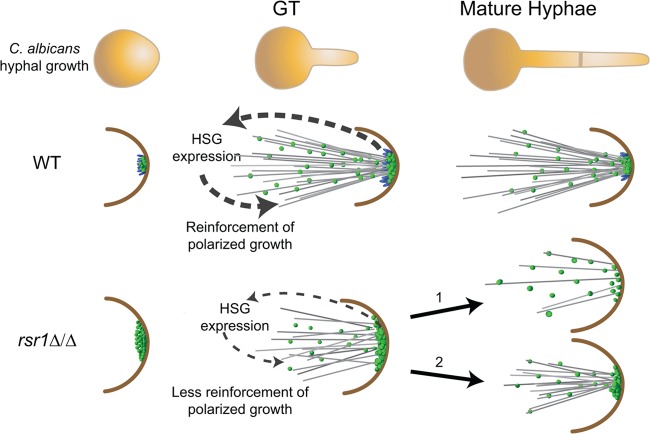
Fig 6.
Model of how Rsr1 impacts the hyphal morphogenesis developmental program. In WT strains, Rsr1 (blue spheres) limits the amount of Cdc42-GTP (green spheres), focuses the distribution of Cdc42 activity during germ tube growth, and maintains the localization of Cdc42 activity during mature hyphal growth. Focused, tip-localized Cdc42 activity contributes to the induction (in GTs) and maintenance (in mature hyphae) of HSG expression, as well as maintenance of Spk integrity (not pictured). In GTs lacking Rsr1, the amount of tip-localized Cdc42-GTP is elevated relative to the WT but is also more broadly distributed at the hyphal tip. The diffuse localization of Cdc42 activity provides weak feedback and results in decreased HSG expression, as well as unregulated (excessive) delivery of Spk-associated components (not pictured) to the hyphal tip. In mature hyphae lacking Rsr1, some cells can no longer localize Cdc42 activity effectively at hyphal tips (pathway 1), whereas others in the population (i.e., those with Cdc42 distributions similar to the wild type) are able to maintain localization of Cdc42 activity, Spk integrity (not pictured), and polarized hyphal growth (pathway 2).