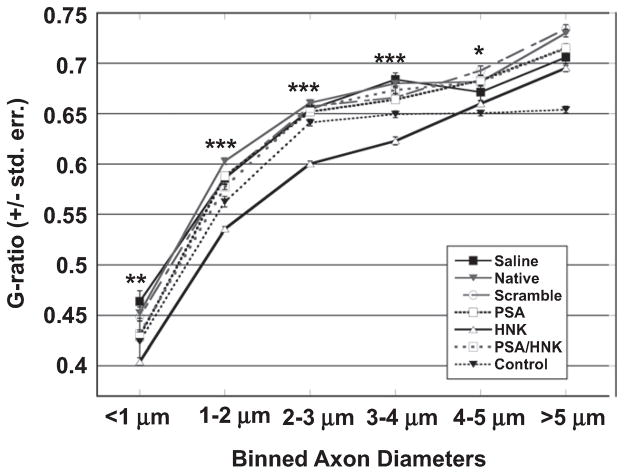
Fig. 6.
Effect of HNK-coupled hydrogels on g-ratio distribution in femoral nerve cross-sections. Measured g-ratios were binned with respect to axon size. Each bin was tested for statistical significance using a one-way ANOVA. Small caliber axons (<1 μm) treated with HNK-coupled hydrogels yield significantly lower g-ratios compared to all other groups (**). Axons between 1 and 4 μm in diameter yielded significantly lower g-ratios in HNK-coupled collagen treated nerves compared to both intact and regenerated nerves (***). Axons between 4 and 5 μm in diameter yielded significantly lower g-ratios than other collagen-treated groups, but not saline-treated or intact nerves (*). No significant differences were found with inclusion of HNK-coupled hydrogels for large caliber axons (>5 μm). Means are reported +/− standard error. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05 using one-way analysis of variance.