FIGURE 1:
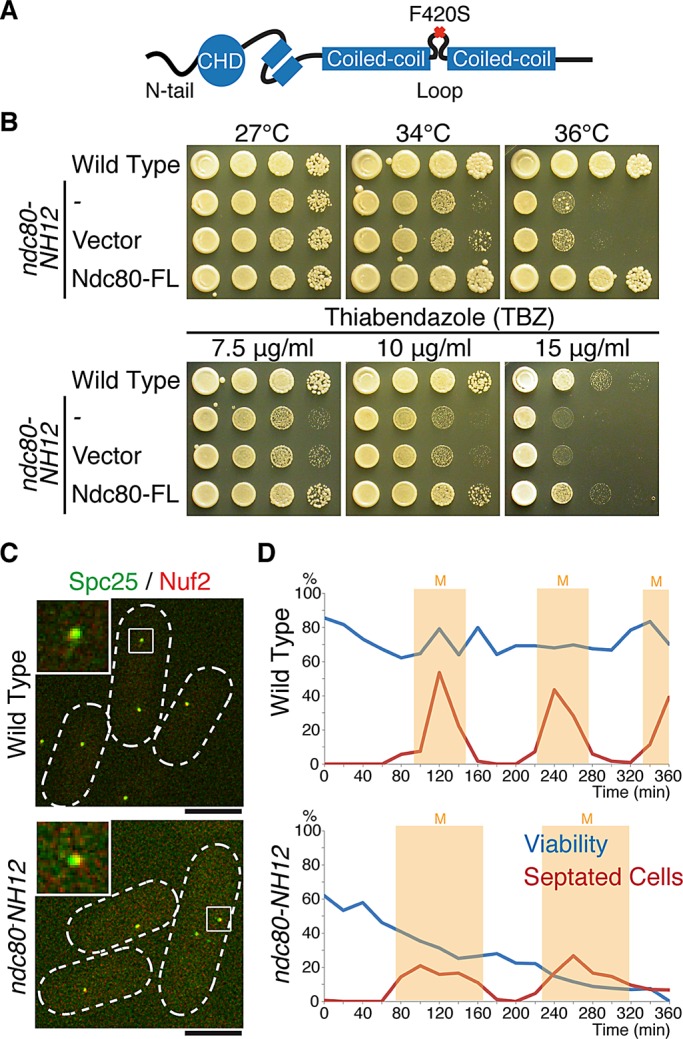
Isolation of the temperature-sensitive ndc80-NH12 mutant, which contains a single point mutation (F420S) within the loop. (A) Schematic presentation of the mutation found in ndc80-NH12. The oval shows the calponin-homology domain (CHD; Wei et al., 2007; Ciferri et al., 2008) preceded by the N-terminal extension; two boxes represent internal coiled-coil domains, which are interrupted by the internal loop. The F420S mutation is located within the loop. See Supplemental Figure S1 for more information on the mutation site. (B) Temperature and thiabendazole sensitivity. Tenfold serial dilutions of wild-type or ndc80-NH12 cells carrying an empty vector (pREP1) or a plasmid carrying the full-length ndc80+ gene (pREP1-Ndc80-FL) were spotted onto rich agar media (5 × 104 cells in the first spot) and incubated at the indicated temperatures for 3 d. The same set of strains were spotted on rich media containing the anti-microtubule drug TBZ (7.5, 10, or 15 μg/ml) and incubated at 27°C for 3 d. (C) Normal kinetochore localization of the Ndc80 complex in the ndc80-NH12 mutant. Wild-type or ndc80-NH12 mutant cells containing Spc25-YFP and Nuf2-mCherry were incubated at 36°C for 4 h. Merged images of fluorescence signals (green for Spc25 and red for Nuf2) are shown. Top left, enlarged images of kinetochore signals (squares). Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Viability of cells (wild type, top; ndc80-NH12, bottom) in synchronous culture analyses. Small G2 cells grown at 27°C were collected by centrifugal elutriation and shifted to 36°C at time 0. At each time point, aliquots of cells were taken and cell number counted. Cell viability (blue lines) was measured by spreading 100–300 cells on rich agar media and incubated at 27°C. The percentage of septated cells (red lines, n > 100) was also counted by staining cells with Calcofluor (a dye staining septa). Light yellow columns mark periods in mitosis.
