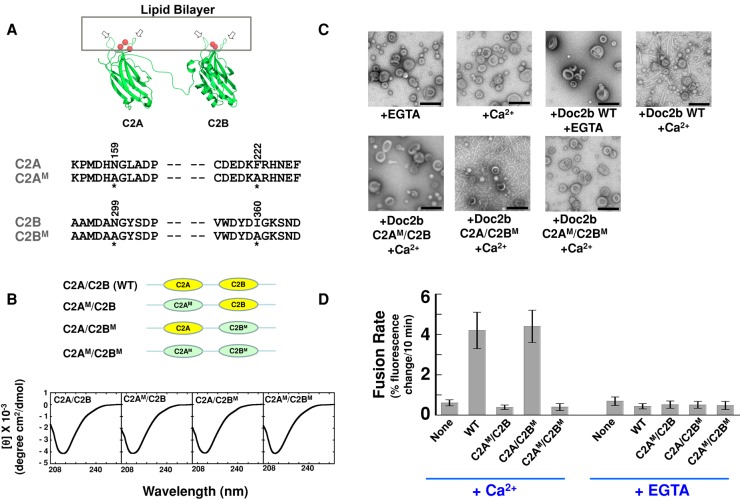
FIGURE 7:
The stimulatory function of Doc2b involves membrane curvature induction. (A) Top, model depicting the binding of Doc2b to the membrane. The two hydrophobic loops (arrows) of the C2 domain insert into the lipid bilayer in the presence of Ca2+ ions (red balls). Modeled from the crystal structure of synaptotagmin-1 C2A domain (PDB: 1BYN) and C2B domain (PDB: 1K5W; Shao et al., 1998; Fernandez et al., 2001). Bottom, sequences of hydrophobic residues in the C2A and C2B domains of Doc2b that are predicted to embed in the lipid bilayer. Mutated residues are indicated with amino acid numbers on the top and asterisks at the bottom. (B) Top, illustrations of WT and mutant Doc2b proteins used in the fusion reactions. WT C2 domains are shown in yellow, and mutant C2 domains are shown in green and labeled with M. Bottom, CD spectroscopic analysis of WT and mutant Doc2b proteins. (C) Electron micrographs showing the bending of Folch liposomes by Doc2b in the presence of 1 mM EGTA or CaCl2. (D) Initial rates of the indicated fusion reactions in the presence of 1 mM EGTA or CaCl2. Each fusion reaction contained 5 μM t-SNAREs and 1.5 μM v-SNARE. Data are presented as percentage of fluorescence change per 10 min. Error bars, SD.