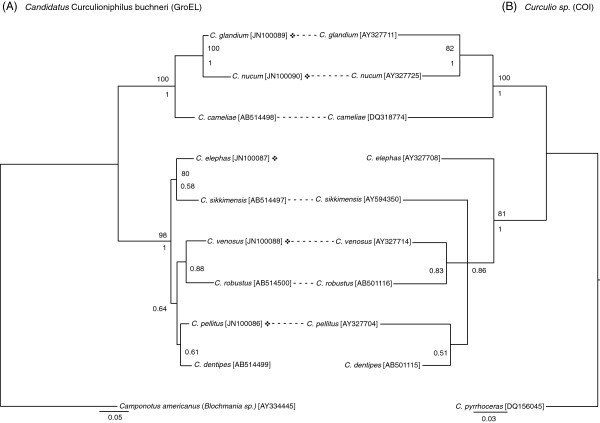
Figure 1.
Phylogenies of the Curculio species and their primary symbiont. The phylogeny of Curculioniphilus is based on the GroEL gene, as its topology was better resolved than that obtained with the 16S rRNA sequence. The Curculio phylogeny is based on a 375 bp sequence of the COI gene. The Bayesian trees are shown, as the Maximum-likelihood trees (not shown) exhibit substantially the same topology (see Methods). The bootstrap values for the maximum-likelihood analysis (100 replicates) and the Bayesian posterior probabilities are shown above and below the nodes only if greater than 50 and 0.50, respectively. The accession numbers of the nucleotide sequences are shown in brackets. Sequences indicated with asterisks were obtained in this study, the other sequences being retrieved from Genbank. The name of each bacterial sequence corresponds to that of its host. The association between the host-symbiont pairs is indicated by dotted line only when significant (i.e., all significant associations were detected with less than a 0.02 risk error except for C. sikkimensis (0.026) and C. venosus (0.034) and their symbionts; see text for the method).