Figure 8.
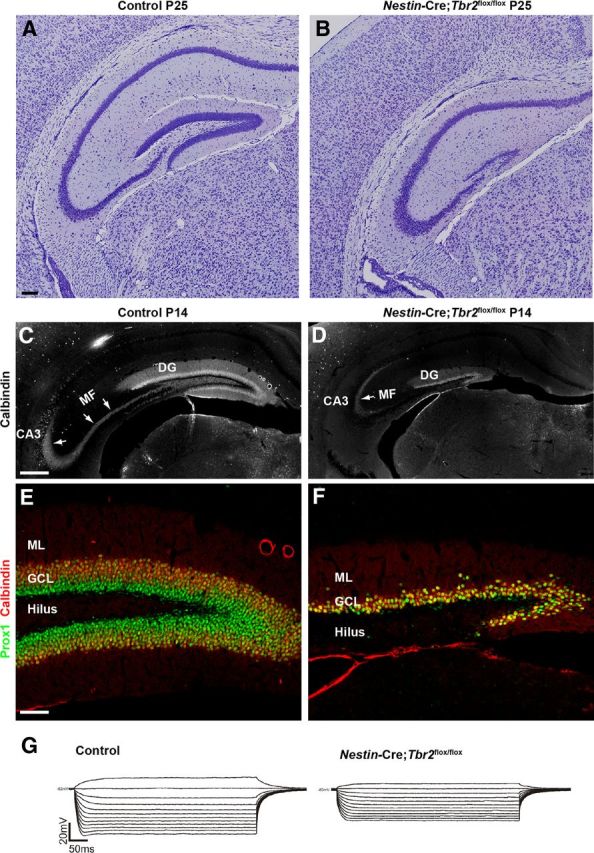
Tbr2 ablation has severe consequences for DG morphogenesis. A, B, By early postnatal development, the DG of control mice is fully formed, whereas the DG of Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice consists only of a truncated and thinned suprapyramidal blade. B, The infrapyramidal blade of the GCL essentially fails to form in Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice. C, The mossy fiber pathway (MF), the main output of the DG granule neurons to CA3, is easily distinguished by immunostaining for calbindin at P14 in control animals (C, arrows). D, In mutant mice, the MF pathway is greatly reduced (D, arrow) because of the decrease in DG size. E, F, The cells that remain in the DG of Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice appear to be granule neurons as evidenced by their expression of Prox1 and calbindin. However, the number of granule neurons populating the DG is clearly greatly reduced in mutant mice (F) compared with controls (E). G, Representative I-V curves from control and Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice illustrate that input resistance is significantly decreased in granule neurons remaining in the reduced DG of mutant mice compared with controls. Scale bars: A, 100 μm; C, 100 μm; E, 100 μm.
