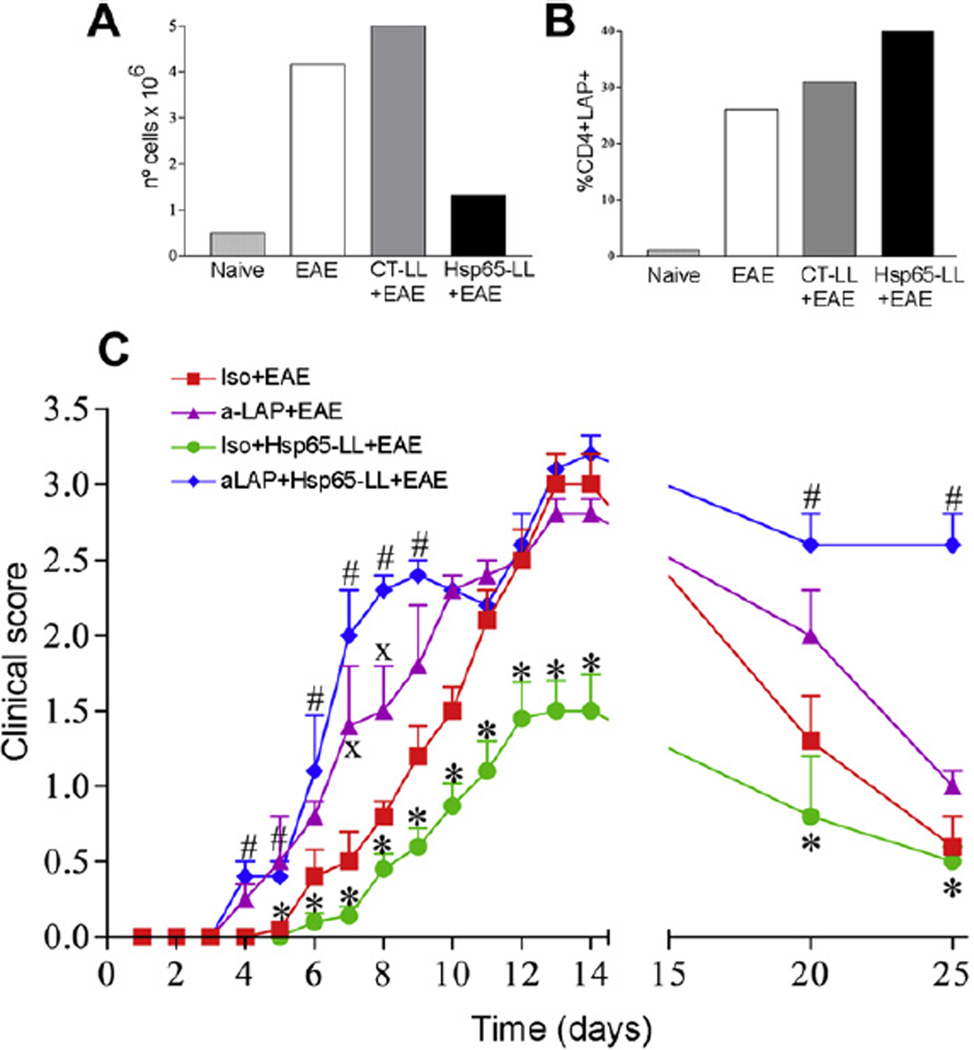
Fig. 6.
The modulatory effect of M. leprae-Hsp65-producing L. lactis in EAE development was dependent on LAP+ regulatory T cells. (A–B) M. leprae-Hsp65-L. lactis-fed mice had increased frequency of CD4+Foxp3+LAP+ Treg cells in the spinal cord. C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP-knock-in mice were fed or not (Naïve) medium (EAE), control (CTLL+EAE) or M. leprae-Hsp65-producing L. lactis (Hsp65-LL+EAE) for four days and EAE was induced ten days later. After 14 days, mice were killed and spinal cords removed. (A) Bar graph is shown as counting of a pool of mononuclear cells from spinal cords of 5 mice/group in a Neubauer chamber. (B) Cells were stained with PE-anti-CD4, Bio-LAP and CY-STV. CD4+ cells were gated. Bar graph is shown as counting pool of lymphocytes expressing LAP and Foxp3 from spinal cords of 5 mice/group. (C) Pretreatment of M. leprae-Hsp65-producing L. lactis fed mice with anti-LAP dampens its prevention EAE. C57BL/6 mice were concomitantly fed medium or M. leprae-Hsp65-producing L. lactis for four days and 20 µg/mouse of intraperitoneally injected anti-LAP (aLAP+EAE, aLAP+Hsp65-LL+EAE) or isotype control rat anti-mouse IgG1; Iso+EAE, Iso+Hsp65-LL+EAE) at day 1, 3 and 5. EAE was induced 1 day later. The course of EAE is shown as mean EAE score ± SEM. n = 5 mice/group; ANOVA, post-test Tukey. *Statistically different from Iso+EAE (except at days 20 and 25), aLAP+EAE and aLAP+Hsp65-LL+EAE groups. #Statistically different from Iso + Medium + EAE group. XStatistically different from aLAP + EAE group; p < 0.05.