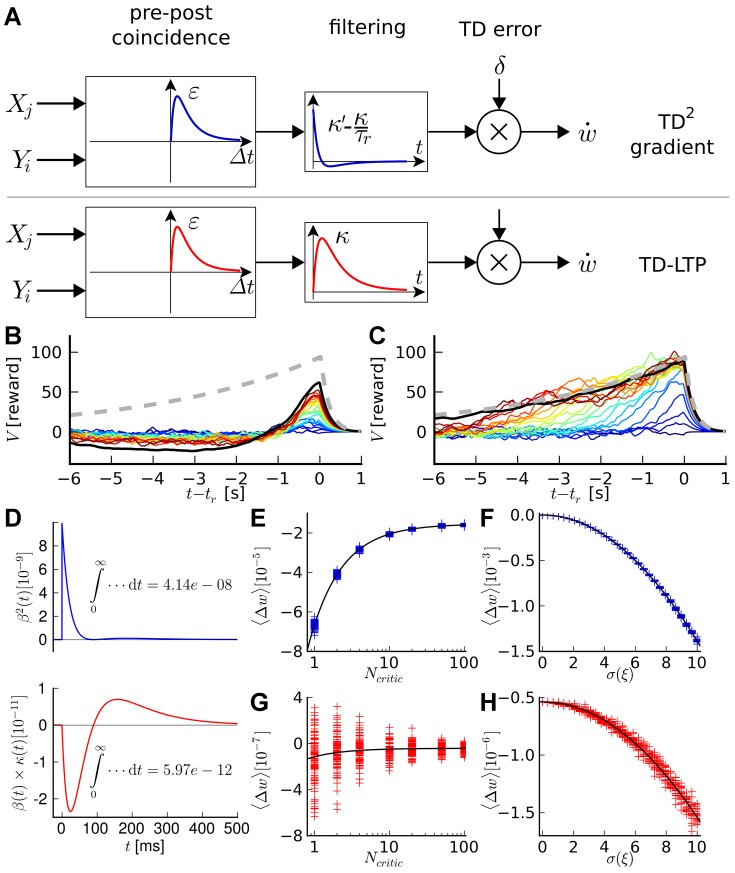
Figure 8. Alternative learning rule and nuisance term.
A: Schematic comparison of the squared TD gradient learning rule of Eq. 46 and TD-LTP, similar to Figure 2A. B: Linear track task using the squared TD gradient rule. Same conventions as in Figure 2C. C: linear track task using the TD-LTP rule (reprint of Figure 2C for comparison). D: Integrands of the disturbance term for Poisson spike train statistics. Top: squared TD gradient rule. Bottom: TD-LTP rule. In each plot the numerical value under the curve is given. This corresponds to the contribution of each presynaptic spike to the nuisance term. E: Disturbance term dependence on 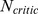 for the squared TD gradient rule. The mean weight change under initial conditions on an unrewarded linear track task with frozen weights, using the squared TD gradient learning rule, is plotted versus
for the squared TD gradient rule. The mean weight change under initial conditions on an unrewarded linear track task with frozen weights, using the squared TD gradient learning rule, is plotted versus 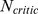 , the number of neurons composing the critic. Each cross corresponds to the mean over a 200s simulation, the plot shows
, the number of neurons composing the critic. Each cross corresponds to the mean over a 200s simulation, the plot shows  crosses for each condition. The line shows a fit of the data with
crosses for each condition. The line shows a fit of the data with  , the dependence form suggested by Eq. 50. F: Same as E, for critic neurons using the TD-LTP learning rule. G, H: Same experiment as E and F, but using a rate neuron model with Gaussian noise of mean 0 and variance
, the dependence form suggested by Eq. 50. F: Same as E, for critic neurons using the TD-LTP learning rule. G, H: Same experiment as E and F, but using a rate neuron model with Gaussian noise of mean 0 and variance 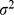 . The line shows a fit with
. The line shows a fit with  , the dependence form suggested by Eq. 50.
, the dependence form suggested by Eq. 50.