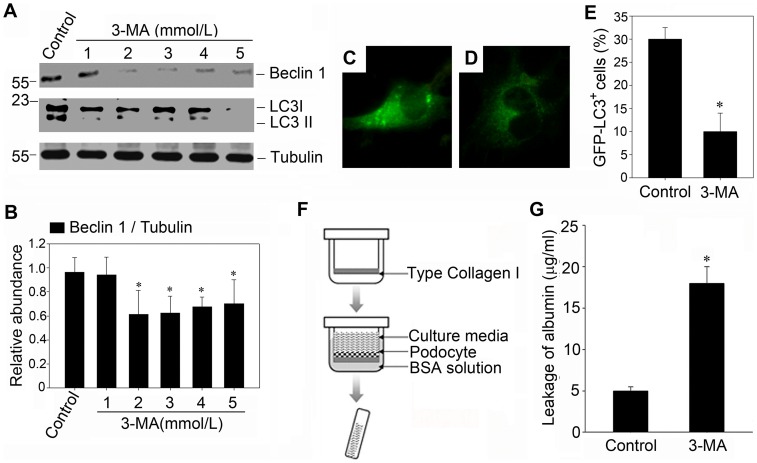
Figure 2. Inhibition of basal autophagy impairs the filtration barrier function of podocyte monolayer.
(A): Western blot analysis confirms the inhibitory effect of 3-MA on autophagy in culture podocytes. Mouse podocytes were incubated with increasing amounts of 3-MA for 24 hours. (B): Graphical presentation shows the relative abundances of Beclin-1 after normalization with α-tubulin. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. normal control; (C and D): Fluorescence staining of GFP-LC3 (400× magnification) in response to 3-MA treatment. Following transfection with GFP-LC3 plasmid as described in Materials and Methods, cells were treated without or with 3-MA (2 mmol/L) for 24 hours. (C): control group; (D): podocytes incubated with 3-MA for 24 hours. (E): Quantification of GFP-LC3 dotted cells after 3-MA treatment. A minimum of 100 GFP-LC3–transfected cells were counted. * P<0.05 vs. control; (F) Schematic depiction of the paracellular permeability influx assay. Podocyte monolayer on collagen-coated transwell filters was incubated without or with 3-MA (2 mmol/L) for 24 h, and albumin permeability across podocyte monolayer was then determined. (G): Graphic presentation of the albumin influx across the podocyte monolayer. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * P<0.05 vs. control.