Figure 3. Recruitment of the negative elongation factor NELF to the c-Fos locus requires CTR9.
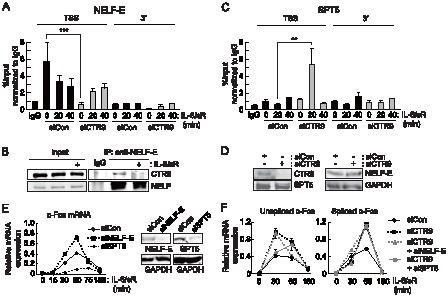
Cells were transfected with control or CTR9 siRNA and treated with IL-6 and IL-6sR (20 ng/ml each) for the indicated length of time. ChIP analyses were performed with soluble chromatin using the antibodies indicated, and the bound DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR using primers specific to c-Fos. Antibodies specific to NELF-E (A), or SPT5 (C), were used. B, Cells were treated with IL-6 and IL-6sR (20 ng/ml each) for 30 minutes and lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-NELF-E antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by western blot analysis. D, Cells were transfected with either control siRNA or CTR9 siRNA. Approximately 48 hours later, protein levels of CTR9, SPT5, NELF-E, and GAPDH were detected by western blot analysis. E, Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated with IL-6 and IL-6sR (20 ng/ml each) for the indicated time period. The c-Fos mRNA induction level was measured by RT-qPCR. E, NELF-E and SPT5 knockdown efficiencies were measured by RT-qPCR (Left) and western blot analysis (Right). mRNA expression levels were normalized to β-Actin. F, Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated with IL-6 and IL-6sR (20 ng/ml each) for the indicated time period. Expression levels were normalized to β-Actin. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Student's t test. Error bars represents SD (n = 3).
