Fig. 1.
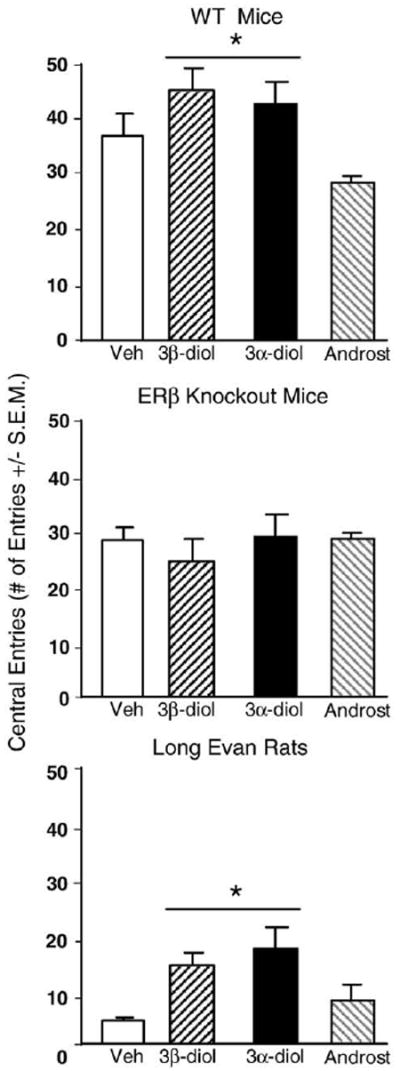
Represents mean central entries in the open field for: wildtype (WT) mice (top) administered acute vehicle control (white bar; n=15), 3β-diol (horizontally-striped bar; n=11), 3α-diol (black bar; n=13), or androsterone (androst; gray-stripe bar; n=12); to ERβ receptor knockout (βERKO) mice (middle) administered acute vehicle control (white bar; n=21), 3β-diol (horizontally-striped bar; n=34), 3α-diol (black bar; n=34), or androsterone (androst; gray-stripe bar; n=29); and to rats (bottom) administered acute vehicle control (white bar; n=22), 3β-diol (horizontally-striped bar; n=26), 3α-diol (black bar; n=25), or androsterone (androst; gray-stripe bar; n=25). Rats and WT mice administered 3α-diol or 3β-diol had significantly more central entries than animals administered androsterone or vehicle. * Denotes significant difference (p<.05).
