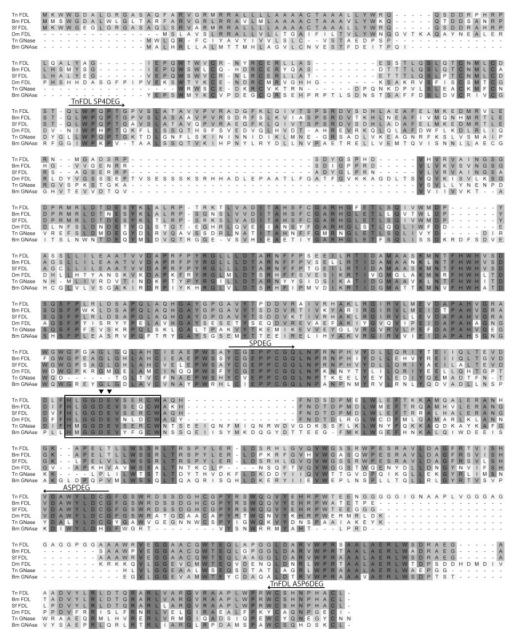
Figure 4. Multiple sequence alignment of insect β-N-acetylglucosaminidases.
This Figure shows an alignment of the predicted amino acid sequences of BmFDL, TnFDL, SfFDL, DmFDL, and other cloned β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (GNase) sequences. The shading is proportional to the degree of amino acid conservation. The boxed region indicates the family 20 glycosyl hydrolase catalytic motif HXGGDEVXXXCW. The solid triangles indicate the aspartate residue likely to stabilize the transition state and the glutamate residue likely to serve as a proton donor during hydrolysis.26 The arrows above the sequences indicate the peptides targeted by degenerate primers used in the degenerate and semi-degenerate PCR reactions to isolate the Tn-fdl gene (see Supporting Information Table 1 for the nucleotide sequences). The amino acid sequences used in this alignment include: Tn FDL (FJ695479): Trichoplusia ni processing GNase (this study), Bm FDL (FJ695481): Bombyx mori processing GNase (this study), Sf FDL (ACA30398): Spodoptera frugiperda processing GNase,21 Dm FDL (Q8WSF3): Drosophila melanogaster processing GNase,20 Bm GNAse (BAF52531): Bombyx mori BmGlcNAcase1, a non-specific GNase,27 Tn GNase (AAL82580): an uncharacterized, putative Trichoplusia ni GNase. Amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalX 2.0.10 with the default settings and the image was generated using DSGene 1.5.