Figure 1.
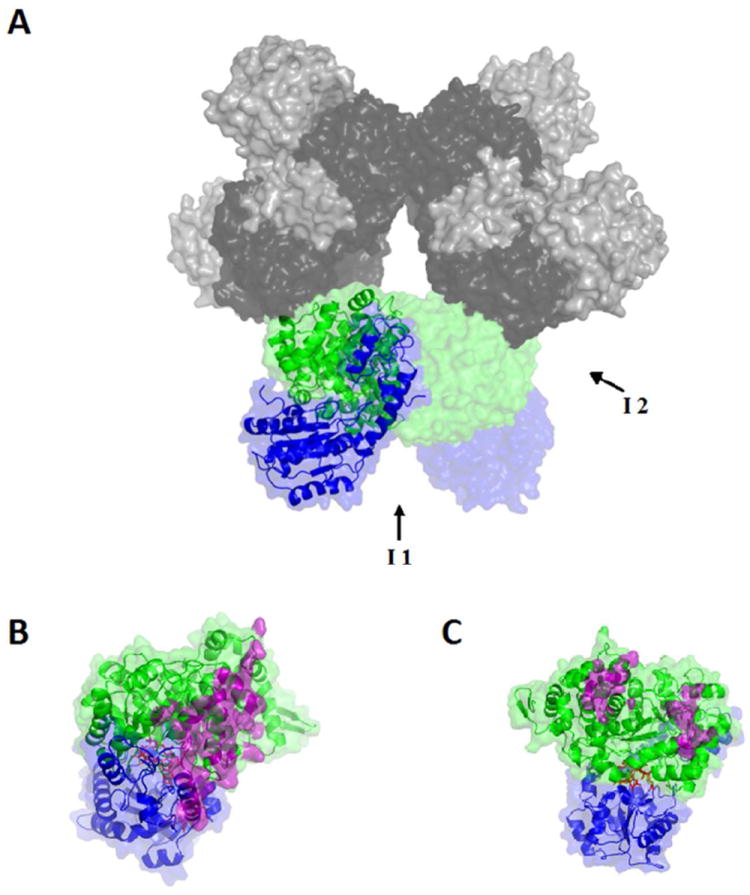
Surface and secondary structure representations of the homology modeled structure of S. typhimurium EAL. (A) The [(EutB-EutC)2]3 EAL oligomer. One (EutB-EutC)2 heterodimer is shown as green (EutB subunits) and blue (EutC subunits), and other two heterodimers in grey tone (EutB, dark grey; EutC, light grey). (B and C) Two EutB-EutC heterodimers, that compose one (EutB-EutC)2 homodimer. EutB is colored green and EutC is blue. (B) The intra-heterodimer interface (denoted I1, in panel A), with residues involved in the contact surface represented in purple. (C) The inter-heterodimer interface (denoted I2, in panel A), with residues involved in the contact surface represented in purple.
