Fig 6.
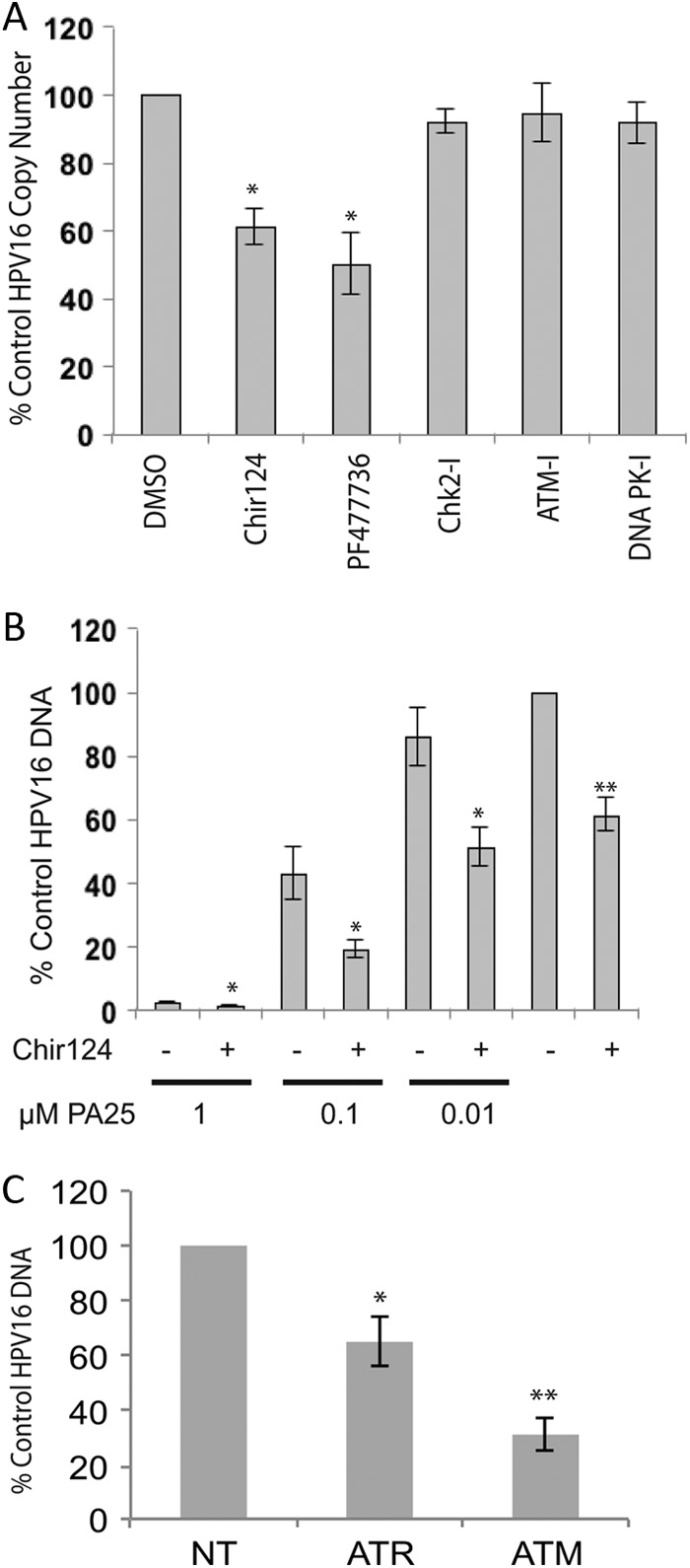
The effects of inhibitors or siRNA acting in the ATR/Chk1 or ATM/Chk2 pathways on W12E cell HPV episomal DNA. (A) W12E cells treated for 48 h with 10 μM ATM inhibitor (ATM-I; Tocris catalog no. KU55933), 5 μM Chk2 inhibitor II (Chk2-I; catalog no. Sigma C3742), or 1 μM DNA-PK inhibitor (DNA PK-I; Tocris catalog no. NU7441) displayed no changes in episome levels relative to control cells. In contrast, 200 nM Chk1 inhibitor PF477736 (Axon Medchem; catalog no. 1379) or Chir124 (Axon Medchem; catalog no. 1636) significantly reduced episome levels compared to vehicle-treated cell results (n = 6; *P < 0.01). (B) Chk1 inhibitor Chir124 significantly reduces HPV16 episomes in an additive manner with PA25 as measured by Q-PCR. W12E cells were treated with 200 nM Chir124 in the presence of increasing PA25 concentrations or 0.1% DMSO vehicle control for 48 h. Statistically significant Chir124 effects are indicated by asterisks: **, Chir124 versus DMSO control; *, aphidicolin plus PA25 versus PA25 alone; n = 6; P ≤ 0.01. (C) siRNA knockdown of ATR or ATM significantly reduces HPV16 episome levels. W12E cells were treated with 100 nM ATR, ATM, or nontargeting siRNA (NT) for 72 h and episomes quantified by Q-PCR. Experimental replicates were analyzed against NT-control siRNA replicates. *, n = 6, P = <0.01, error bars represent standard deviations; **, n = 3 independent experiments with 3 replicates each, P = <0.01, error bars represent standard errors of the means.
