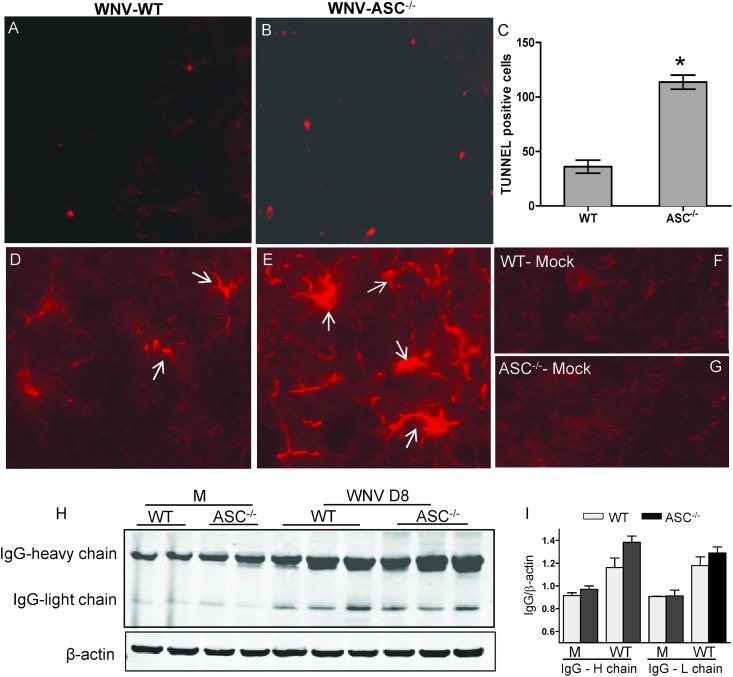
Fig 7.
Increased neuropathology in the brains of ASC−/− mice. (A and B) A TUNEL assay was conducted on PFA-fixed brain sections from WNV-infected WT (A) and ASC−/− (B) mice at day 8 after infection to evaluate neuronal apoptosis. The photomicrographs show representative images obtained from two independent experiments (n = 4 per group). (C) Quantitative representation of TUNEL-positive cells from 15 different brain areas per section from two independent experiments (n = 4 per group). The number of TUNEL-positive cells was significantly higher in the ASC−/− mouse brain. *, P < 0.05. The data are expressed as means ± standard deviations. (D and E) PFA-fixed brain sections from WNV-infected WT (D) and ASC−/− (E) mice at day 8 after infection were stained for GFAP, a marker for activated astrocytes. The immunoreactivity of GFAP was higher in WNV-infected ASC−/− mice. White arrows indicate activated astrocytes. (F and G) The sections from mock-infected WT (F) and ASC−/− (G) mice did not show reactivity for GFAP. The photomicrographs show representative images obtained from two independent experiments (n = 4 per group). (H) Brain lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting was conducted to detect heavy and light chains of IgG as a marker of increased BBB permeability. (I) Quantitative analysis of Western blot results. All values are relative to β-actin and are representative of four mice per group from at least two independent experiments.