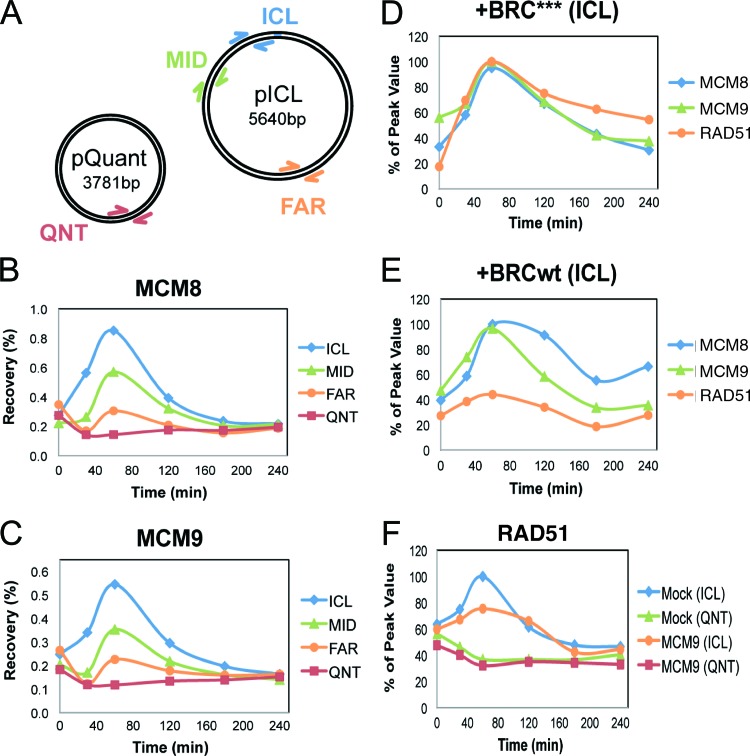
Fig 8.
MCM9 is required for efficient RAD51 binding to ICLs in Xenopus egg extracts. (A) Plasmid schematic showing the locations of different primer pairs used to analyze protein recovery during ChIP: ICL (25 to 132 bp away from the cross-link), MID (663 to 775 bp away), FAR (2,523 to 2,622 bp away), and QNT (undamaged control plasmid). (B and C) ChIP was used to measure the kinetics of MCM8 (B) or MCM9 (C) recruitment during replication of pICL and pQuant. A representative sample of three separate experiments is shown. (D and E) Inhibition of RAD51 loading does not interfere with MCM8 or MCM9 recruitment to the ICL. ICL localization of MCM8, MCM9, and RAD51 was measured by ChIP during replication in extracts supplemented with 14 μM BRC*** (D) or BRCwt peptide (E). (F) MCM9 depletion interferes with the accumulation of RAD51 at the ICL. pICL and pQuant were replicated in mock- or MCM9-depleted extracts, and recruitment of RAD51 was analyzed by ChIP.