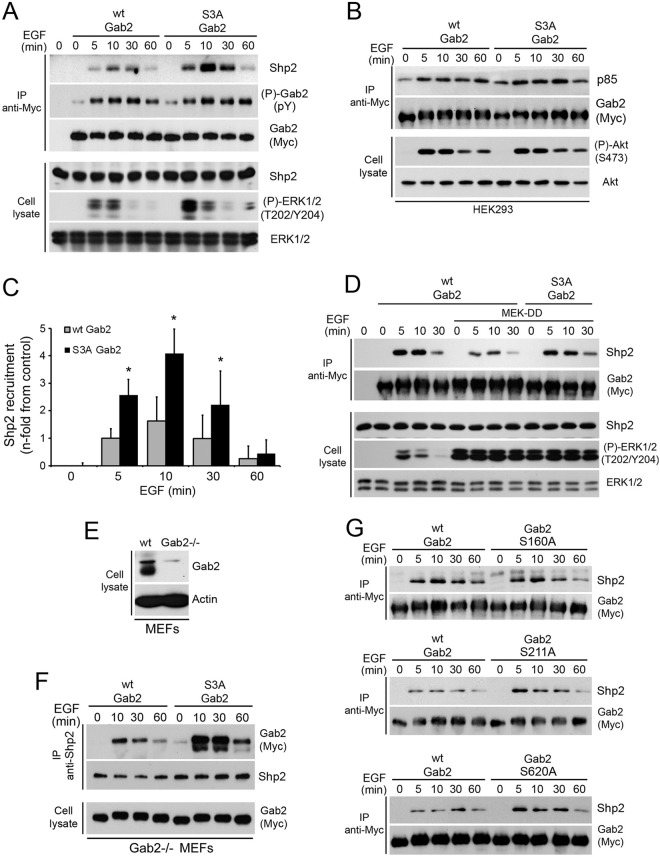
Fig 6.
A Gab2 mutant that cannot be phosphorylated on Ser160/211/620 promotes Shp2 recruitment. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with wt Myc-Gab2 or the S3A mutant, serum starved overnight, and stimulated with EGF (25 ng/ml) over a time course. Associated Shp2 within Gab2 immunoprecipitates was evaluated by immunoblotting. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with wt Myc-Gab2 or the S3A mutant, serum starved overnight, and stimulated with EGF (25 ng/ml) over a time course. Associated p85 was evaluated within Gab2 immunoprecipitates by immunoblotting, as well as Akt phosphorylation at Ser473. (C) The bar graph shows the relative Shp2 recruitment quantified by densitometry (as described in Materials and Methods) from three independent experiments similar to the one whose results are shown in panel A. The data are expressed as the mean fold increase in Shp2 recruitment comparing immunoprecipitations with wt Gab2 and the S3A mutant. Results are means ± SEMs. One-tailed unequal variance Student's t test P values are indicated for a comparison of the means of the wt and mutant (S3A) Gab2 levels. *, P < 0.01. (D) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with wt Myc-Gab2 or the S3A mutant, with or without MEK-DD, serum starved overnight, and stimulated with EGF (25 ng/ml) over a time course. Shp2 recruitment was evaluated as described for panel A. (E) Wild-type and Gab2-deficient MEFs were evaluated for the presence of endogenous Gab2 by immunoblotting on total cell lysates. (F) Gab2-deficient MEFs stably expressing wt Gab2 or the S3A mutant were seeded at a similar density and serum starved overnight, prior to EGF (25 ng/ml) stimulation over a time course. Associated Myc-Gab2 was assayed within endogenous Shp2 immunoprecipitates by immunoblotting. (G) HEK293 cells were transfected with wt Myc-Gab2 or each of the Gab2 mutants (S160A, S211A, or S620A), serum starved overnight, and stimulated with EGF (25 ng/ml) over a time course. Associated Shp2 was evaluated within Gab2 immunoprecipitates by immunoblotting.