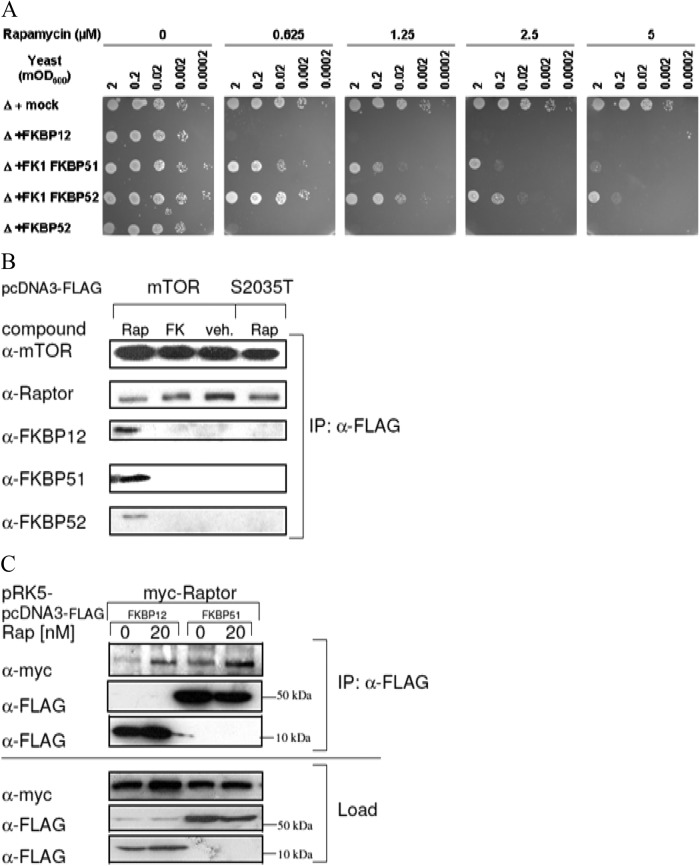
Fig 3.
TOR-FKBP interactions in eukaryotic cells. (A) Overexpression of FKBP homologs restores rapamycin sensitivity in yeast cells. Yeast strain ΔFPR1p, lacking FKBP12, was transformed with plasmids encoding human FKBP12, FKBP51 FK1, FKBP52 FK1, or full-length FKBP52 under the control of the Gal promoter. A 1:10 dilution series of the resulting strains was spotted onto yeast minimal medium plates lacking histidine with 0.2% galactose as the carbon source with or without supplementation with the indicated concentrations of rapamycin and grown for 3 to 4 days at 30°C. (B) mTOR interacts with FKBP12, FKBP51, and FKBP52 in a rapamycin-dependent manner. HEK293 cells were transfected with a FLAG-mTOR or FLAG-mTOR-S2035T expression plasmid. At 30 min prior to lysis, rapamycin (Rap), FK506 (FK) (final concentration, 25 nM each), or the dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle (veh.) was added. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody, and the eluates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (C) FKBP12 and FKBP51 interact with the mTORC1 component Raptor. HEK293 cells were transfected with myc-Raptor and FLAG-FKBPs, starved, and stimulated with FBS in the absence or presence of 20 nM rapamycin for 60 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. Beads were washed four times with CHAPS-containing lysis buffer and eluted by boiling with SDS sample buffer for 5 min. Supernatants were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Expression of FKBPs was induced by SG medium.