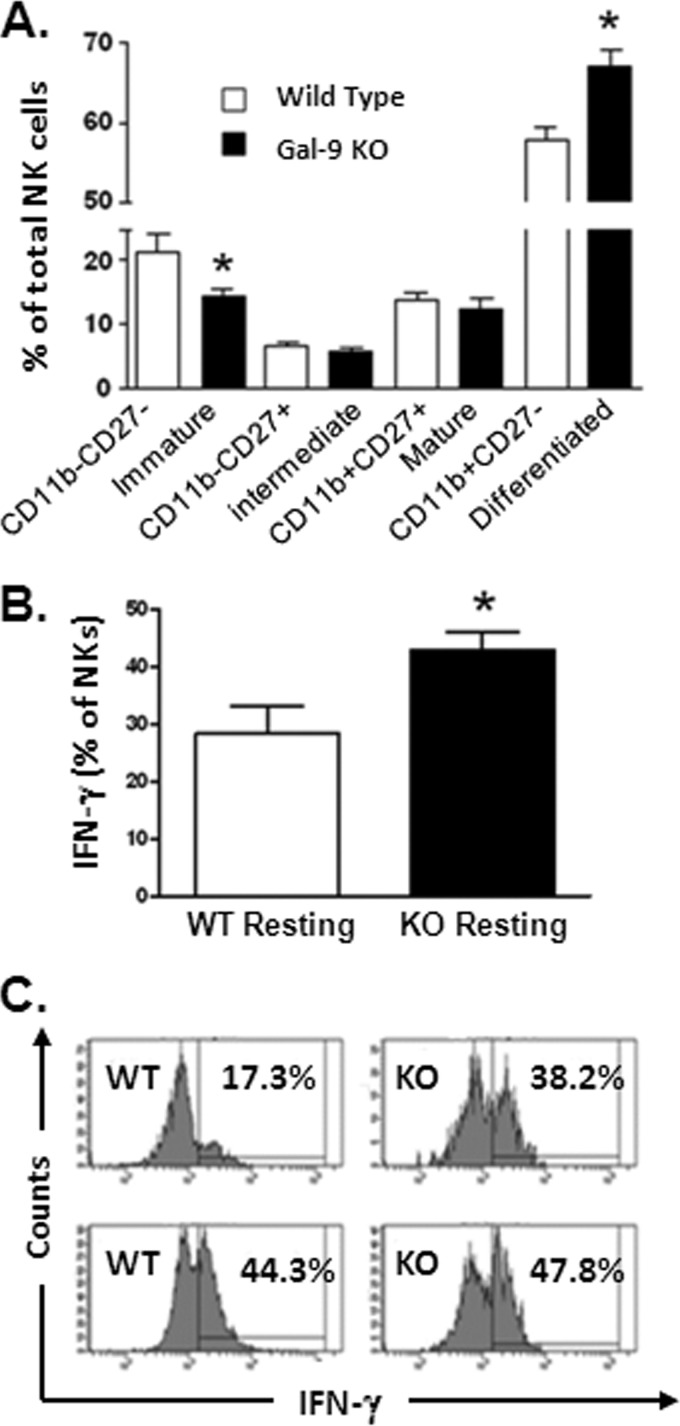
Fig 8.
MCMV infection in Gal-9 KO mice. (A) Hepatic mononuclear cells were isolated from the livers of control (n = 5) and Gal-9 KO (n = 5) mice after 4 days of infection with MCMV (as described in Materials and Methods). Flow-cytometric analysis was used to identify NK cells (CD3e− NK1.1+), and the expression of CD11b and CD27 on NK cells to assess the maturation stage was analyzed as described previously (45) and in Results. Gal-9 KO mice have a lower proportion of immature and a higher proportion of fully differentiated NK cells (denoted by an asterisk). (B) Hepatic mononuclear cells were rested overnight in the presence of BFA and stained for intracellular IFN-γ (as described in Materials and Methods). Spontaneous IFN-γ production by hepatic NK cells was significantly higher in Gal-9 KO mice than in wild-type controls. The bars represent medians ± interquartile ranges. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to calculate P values between control (WT) and KO groups. (C) Representative flow-cytometric histograms of spontaneous (upper) and IL-12/IL-18-stimulated (bottom) IFN-γ production by hepatic NK cells is shown. The numbers represent the percentages of total NK cells positive in control (WT) and Gal-9 KO mice. The level of IFN-γ production by WT and KO hepatic NK cells is similar with cytokine stimulation.