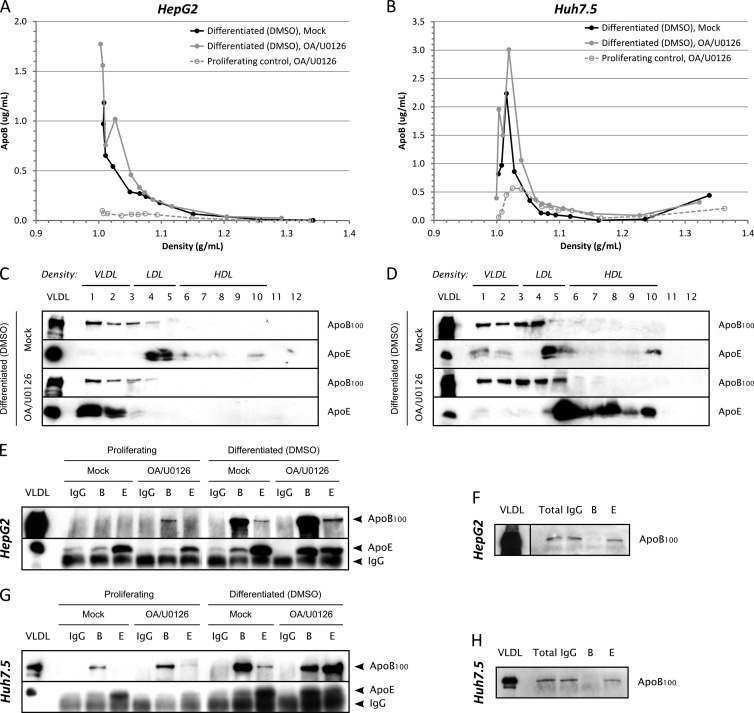
Fig 1.
apoB100 and apoE secretion in partially redifferentiated hepatoma cells. HepG2-CD81 (panels A, C, E, and F) or Huh7.5 (panels B, D, G, and H) cells were seeded on 100-mm petri dishes. At confluence, cells were exposed for 3 days to 2% DMSO to promote their differentiation and incubated another 24 h with medium without serum containing 2% DMSO, 10% (vol/vol) OA-BSA, and 1 μM U0126 (OA/U0126) or containing 2% DMSO and 10% (vol/vol) BSA (Mock). Supernatants (10 ml) were harvested, filtered (0.45-μm pore size), and subjected either to density separation on iodixanol-sucrose gradients (panels A to D) or to immunoprecipitation (panels E to H). (A) ApoB quantification using ELISAs in each fraction of the density gradient for DMSO-differentiated HepG2-CD81 cells. apoB secretion in subconfluent proliferative and OA/U0126-treated cells was also quantified for comparison (dashed gray curve). (B) apoB quantification using ELISAs in each fraction of the density gradient for DMSO-differentiated Huh7.5 cells. apoB secretion in subconfluent proliferative and OA/U0126-treated cells was also quantified for comparison (dashed gray curve). (C) apoB100 and apoE immunoblotting in each fraction for DMSO-differentiated HepG2-CD81 cells. (D) apoB100 and apoE immunoblotting in each fraction for DMSO-differentiated Huh7.5 cells. (E to H) Immunoprecipitations were performed with 4 μg/ml of anti-apoB100 or anti-apoE antibodies, using protein G-coated magnetic beads, in HepG2-CD81 (E) and Huh7.5 (G) cells. IgG from goat serum was used as a negative control. Immunoprecipitated apoB100 or apoE was detected by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. apoB100 was also detected in total supernatants (Total) and IP flowthrough by immunoblotting to check for immunoprecipitation efficiency (F and H). B, IP with anti-apoB antibodies; E, IP with anti-apoE antibodies; VLDL, control VLDL from human serum.