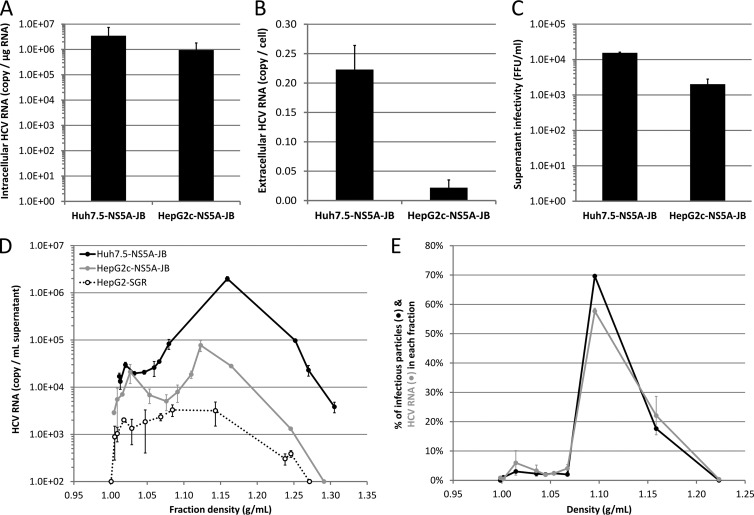
Fig 6.
JB-replicating hepatoma cell lines produce infectious viral particles. Huh7.5-NS5A-JB and HepG2c-NS5A-JB cells were treated for 3 days with DMSO and incubated another 24 h with DMSO, OA, and U0126 to harvest culture supernatants or quantify intracellular viral RNA. (A) Intracellular HCV RNA was quantified by quantitative RT-PCR, and results were normalized for total intracellular RNAs and glucuronidase gene expression. (B) Extracellular HCV RNA was quantified by quantitative RT-PCR, and results were normalized for cell number. (C) Supernatant infectivity was measured as focus-forming units (FFU/ml). Error bars represent standard deviations of three independent experiments. (D) Culture supernatants were loaded on iodixanol-sucrose density gradients, and HCV RNA concentration in each fraction was determined by quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR). Results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (E) HCV RNA or infectious viral particles secreted by HepG2c-NS5A-JB cells are shown in each fraction as a percentage compared to the total amount of HCV RNA or infectious viral particles in the whole gradient, respectively. HCV RNA amount was determined by RT-qPCR. Infectious viral particles were quantified using the TCID50 method. Results are representative of two independent experiments.