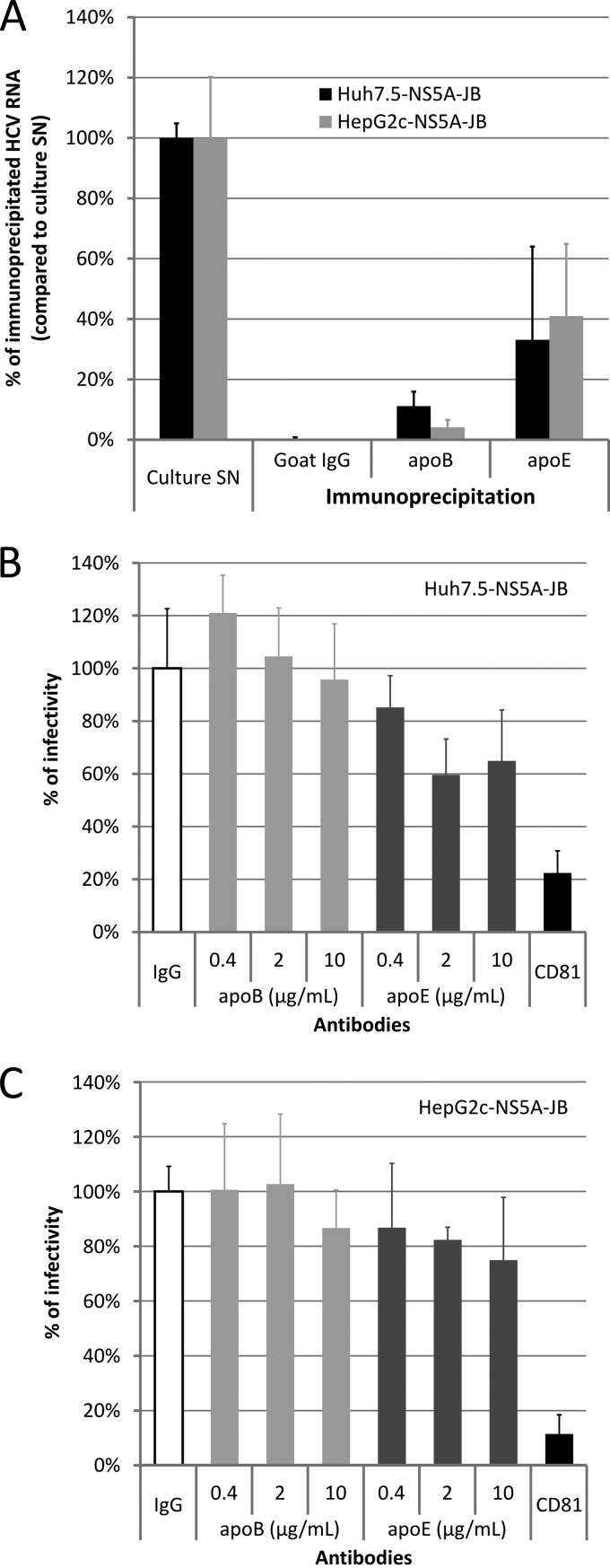
Fig 7.
Characterization of viral particles produced by JB-replicating cells. Huh7.5-NS5A-JB, HepG2-SGR, and HepG2c-NS5A-JB cells were treated for 3 days after confluence with 2% DMSO and incubated another 24 h with serum-free medium containing 2% DMSO, 10% (vol/vol) OA-BSA, and 1 μM U0126. Supernatants were harvested, filtered (0.45-μm pore size), and used for immunoprecipitation (IP) and neutralization experiments. (A) Harvested supernatants from Huh7.5-NS5A-JB and HepG2c-NS5A-JB cells were immunoprecipitated with goat polyclonal anti-apoB or anti-apoE antibodies, using protein G-coated magnetic beads. IgG from goat serum was used for a control. The percentage of HCV IP was assessed by quantifying HCV RNA using RT-qPCR in immunoprecipitated pellets, compared to HCV RNA in the culture supernatant (SN). Error bars represent standard deviations of two independent experiments. (B and C) Supernatants from Huh7.5-NS5A-JB and HepG2c-NS5A-JB cells were incubated for 2 h at room temperature with different concentrations of mouse monoclonal anti-apoB antibody (4G3) or with mouse monoclonal anti-apoE (D6E10). As a positive neutralization control, supernatants were incubated for 2 h at room temperature with 10 μg/ml of mouse monoclonal anti-CD81 antibody (JS81). As a negative control, supernatants were incubated for 2 h at room temperature with 10 μg/ml of IgG from mouse serum. Naïve Huh7.5 cells were then incubated for 4 h at 37°C with supernatant-antibody mixtures and further processed. Cells for CD81 neutralization experiments were incubated with 10 μg/ml of anti-CD81 antibody concomitantly. Cells were washed once with PBS and stained after 3 days for HCV core protein to determine viral titer (FFU). Error bars represent standard deviations of two independent experiments.