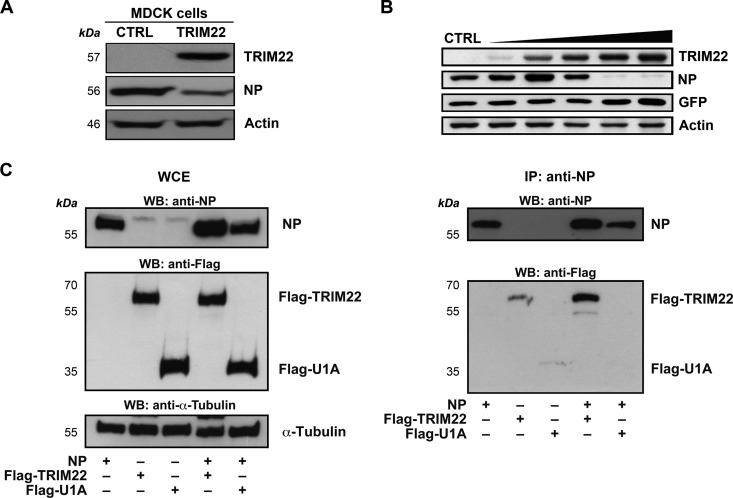
Fig 5.
TRIM22 leads to impaired NP expression through protein-protein interaction. (A) Control and TRIM22-transduced MDCK cells (CTRL and TRIM22, respectively) were infected with A/NewCaledonia/20/99 (H1N1) at an MOI of 0.001, and the levels of viral NP expression were evaluated in WCE obtained 24 h p.i. Actin was used as a normalizer. (B) 293T cells were cotransfected with a fixed amount of both viral NP-expressing plasmid (50 ng) and GFP-expressing plasmid (50 ng) with increasing amounts of TRIM22-expressing plasmid (from 50 to 5,000 ng). WCE were prepared 24 h p.t., and TRIM22, NP, and GFP expression levels were evaluated by Western blotting. Actin was detected as a loading control. These results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) 293T cells were cotransfected with equal amounts (7.5 μg) of an NP-expressing and a Flag-TRIM22-expressing plasmid or a U1A-expressing plasmid as a control. WCE were prepared 48 h p.t., and immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-NP Ab was performed. Input (left) and pulldown product (right) were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of NP, U1A, and TRIM22. α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control on input extracts.