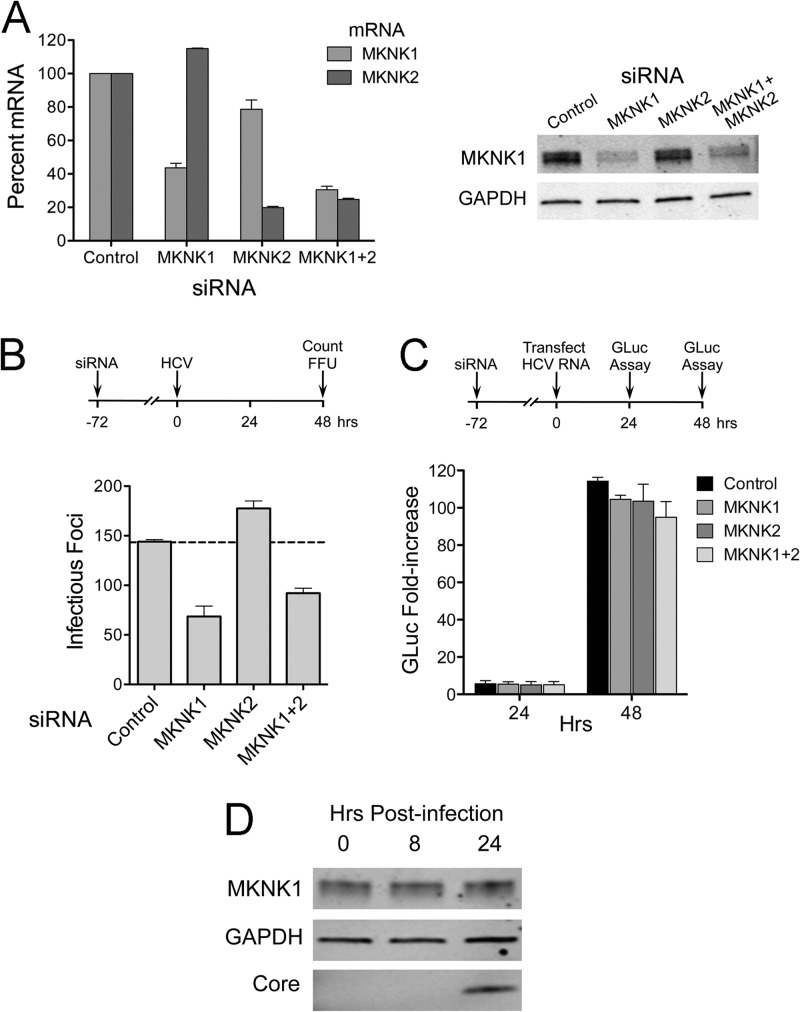
Fig 6.
RNAi-mediated knockdown of MKNK1 inhibits HCV cell entry. (A) (Left) RNAi-mediated decreases in MKNK mRNAs. Total cellular RNA was extracted from cells following transfection with MKNK1- and MKNK2-specific siRNAs and assayed for MKNK1 and MKNK2 mRNAs by qRT-PCR. Means ± SD were calculated from replicate experiments. (Right) Immunoblots of MKNK1 in lysates from siRNA-transfected cells. MKNK2-specific antibody was not available. (B) Number of infectious foci in HJ3-5 virus-inoculated cells following knockdown of MKNK1 and MKNK2. Huh-7.5 cells were infected by HJ3-5 virus 3 days after siRNA transfection. Two days later, foci of infected cells were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence and enumerated. Results shown represent means ± SE from two independent experiments. (C) Effect of MKNK knockdown on HCV RNA replication. Cells were transfected with HJ3-5/GLuc2A RNA 72 h following transfection with the indicated siRNAs. GLuc activities secreted by the transfected cells were measured and plotted as fold change relative to GLuc present 6 h after HCV RNA transfection (33). Means ± SE were calculated from two independent experiments. (D) Immunoblot showing MKNK1 expression in Huh-7.5 cells following infection with HJ3-5 virus (MOI of ∼5). Lysates were prepared at 0 h (before infection) and 8 and 24 h after infection and were subjected to immunoblotting for MKNK1, GAPDH, and HCV core protein.