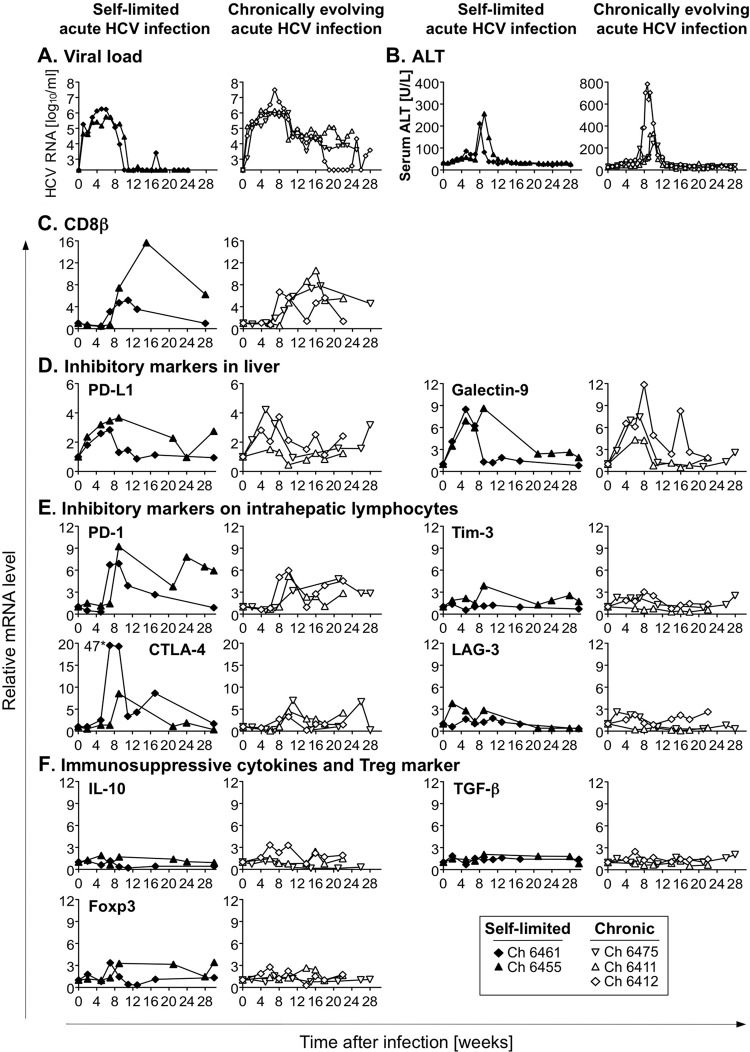
Fig 1.
Intrahepatic mRNA expression levels of T-cell-inhibitory molecules during acute HCV infection. (A to C) Five chimpanzees were intravenously challenged with serum containing 100 chimpanzee 50% infectious doses (CID50) of HCV genotype 1a in a protocol approved by the Public Health Service Interagency Model Committee (National Institutes of Health) and the Animal Care and Use Committee (Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research) at an Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Animal Care-accredited facility (23). Serum HCV RNA titers (A), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (B), and intrahepatic CD8β mRNA levels (C) have previously been reported (23, 24) and are shown for reference purposes. (D to F) Serial liver biopsy specimens were analyzed for mRNA levels of PD-L1 and galectin-9 (D), of PD-1, Tim-3, CTLA-4, and LAG-3 (E), and of IL-10, TGF-β, and Foxp3 (F). Intrahepatic mRNA levels were normalized to mean levels of β-actin, GAPDH, and β7 mRNA as endogenous references and were expressed as fold increases over preinfection levels. The CTLA-4 mRNA value next to the asterisk specifies an off-scale value.