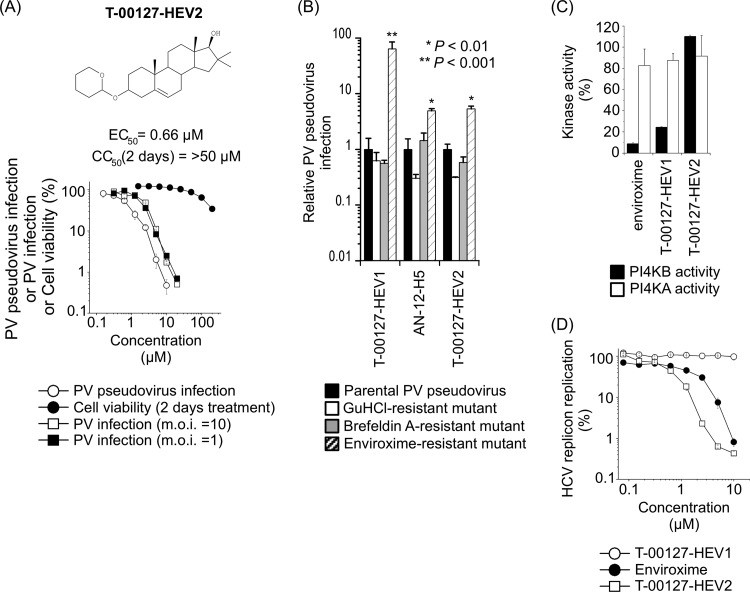
Fig 1.
(A) Characterization of T-00127-HEV2. (Top) Structure of T-00127-HEV2. (Bottom) Inhibitory effect of T-00127-HEV2 on PV pseudovirus and viability of RD cells. PV pseudovirus infection (luciferase assay), viability of cells, or PV1(Mahoney) infection (number of copies of the viral genome at 7 h p.i. in RD cells) in the absence of compounds was taken as 100%. T-00127-HEV2 showed precipitation above 50 μM. (B) Specificity of resistance mutations to T-00127-HEV2. RD cells were infected with PV pseudovirus mutants that have resistance mutations to GuHCl (U4614A), brefeldin A (G4361A plus C5190U), and enviroxime (G5318A) in the presence of antienterovirus compounds: T-00127-HEV1 (3.1 μM), AN-12-H5 (25 μM), and T-00127-HEV2 (6.3 μM). Relative PV pseudovirus infection is shown, where parental PV pseudovirus infection in the presence of each compound was taken as 1. n = 3. (C) Inhibitory effects of enviroxime-like compounds on in vitro activity of PI4KB and PI4KA. In vitro kinase activities were analyzed in the presence of each compound (1 μM) and ATP (10 μM). (D) HCV replicon replication in the presence of enviroxime-like compounds. HCV replicon replication in the absence of compounds was taken as 100%. The error bars indicate standard deviations.