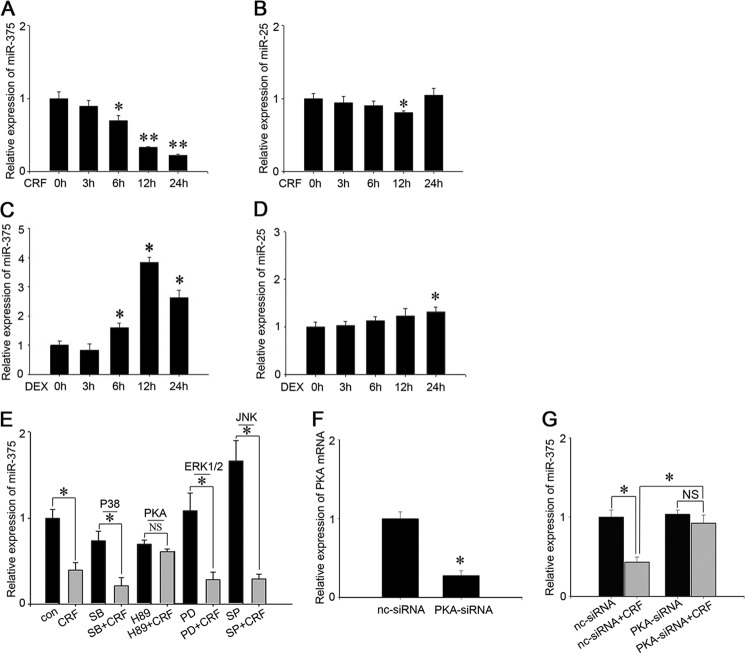
FIGURE 3.
miR-375 is specifically regulated by CRF and DEX in AtT-20 cells. A and B, AtT-20 cells were treated with 100 nm CRF for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively. The expressions of miR-375 and miR-25 were analyzed by real-time PCR and normalized to the U6 transcript level. C and D, AtT-20 cells were treated with 100 nm DEX for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively. The expressions of miR-375 and miR-25 were analyzed by real-time PCR and normalized to the U6 transcript level. Results are means ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant (p > 0.05) versus control (t test). E, the relative level of miR-375 in AtT-20 cells treated with CRF and several different signal pathway inhibitors. The control (con) was a vehicle control (PBS). The inhibitors include, SB-203680 (SB), H89, PD98059 (PD), and SP-600125 (SP). The data are means ± S.E. for multiple separate transfections (n = 3); *, p < 0.05; NS, not significant (p > 0.05) (ANOVA). F, transfection of PKA-specific siRNA detect the PKA mRNA level by real-time PCR. Results are means ± S.E. of three independent experiments; **, p < 0.01 versus cell transfected with nc-siRNA (t test). G, AtT-20 cells were transfected with PKA siRNA or nc-siRNA for 24 h and then added 100 nm CRF and 12 h later detected miR-375 expression level. Data presented as means ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; NS, not significant (p > 0.05) (ANOVA).