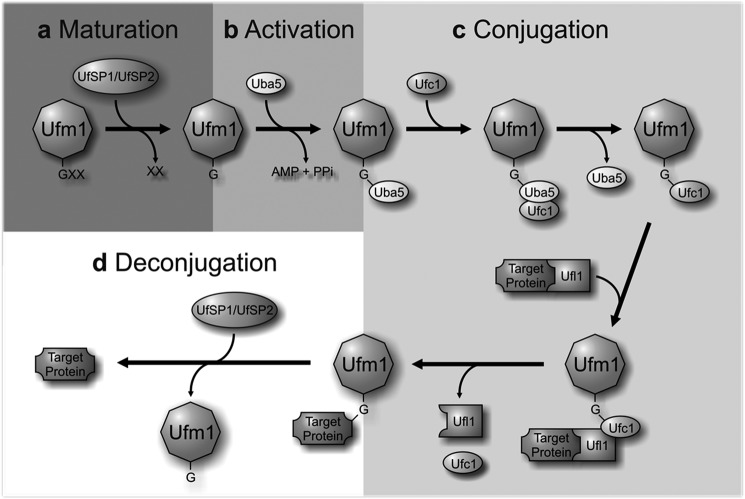
FIGURE 1.
The Ufm1 conjugation pathway. a, maturation. The Ufm1-specific proteases UfSP1 and UfSP2 process the C-terminal extension of the Ufm1 precursor, exposing a conserved glycine residue. b, activation. The mature Ufm1 is activated by Uba5 (E1) in an ATP-dependent manner, forming a high-energy thioester bond. c, conjugation. The activated Ufm1 is then transferred to Ufc1 (E2) in a similar thioester linkage. The E3 enzyme Ufl1 enables the transfer of Ufm1 to the target protein, thereby forming an isopeptide bond between Ufm1 and its substrate. d, deconjugation. The proteases UfSP1 and UfSP2 also mediate the deconjugation of Ufm1.