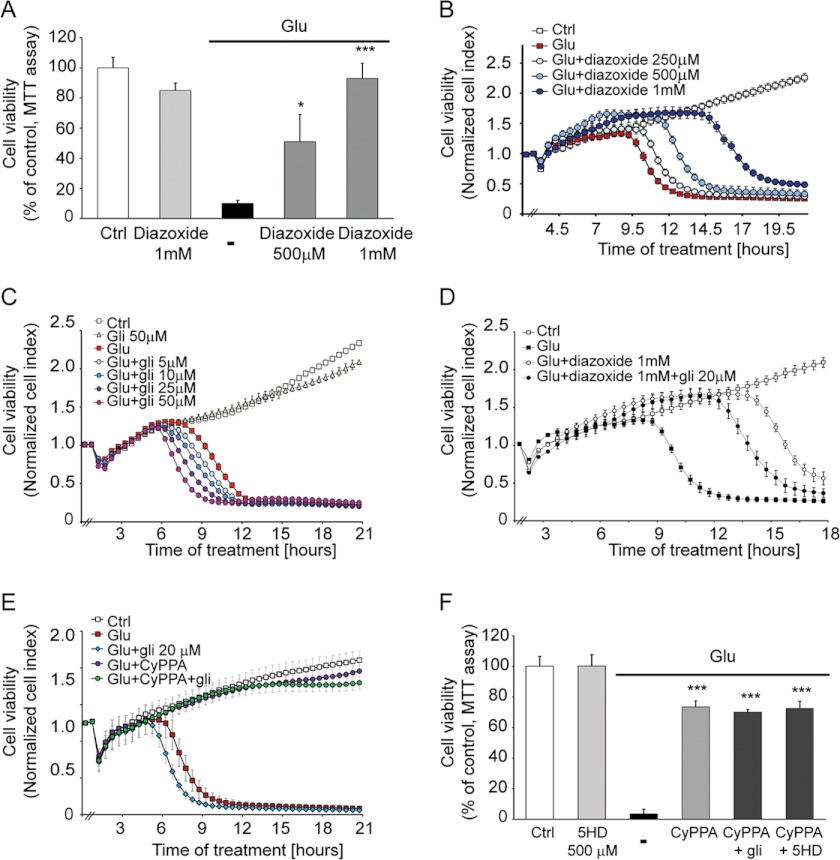
FIGURE 6.
Activation of SK2 channels inhibits oxytosis independently of KATP channel pathways. Cells were treated with different concentrations of diazoxide (250 μm, 500 μm, and 1 mm) and stimulated with glutamate (3 mm). Diazoxide mediated neuroprotection in a dose-dependent manner as analyzed by an MTT assay (14 h following glutamate application) (A) and xCELLigence system (B). (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 versus glutamate-treated neurons were considered to be significant; ANOVA and Scheffé's test; n = 8). C, xCELLigence analysis of HT-22 cells treated with glibenclamide (5–50 μm) in the presence or absence of glutamate (3 mm). The time point of treatment is marked as 0 h in the graph (n = 8). D, xCELLigence analysis of HT-22 cells treated with diazoxide (1 mm) with or without glibenclamide (20 μm) and challenged with glutamate (3 mm). E, xCELLigence analysis of HT-22 cells treated with CyPPA (25 μm) with or without glibenclamide (20 μm) and challenged with glutamate (3 mm). F, MTT assay of cells treated with CyPPA (25 μm) and 5-hydroxydecanoate (5HD) (500 μm) or glibenclamide (20 μm) and stimulated with glutamate (3 mm) (***, p < 0.001 versus glutamate-treated neurons were considered to be significant; ANOVA and Scheffé's test; n = 8). Error bars represent S.D. Ctrl, control.