Fig 5.
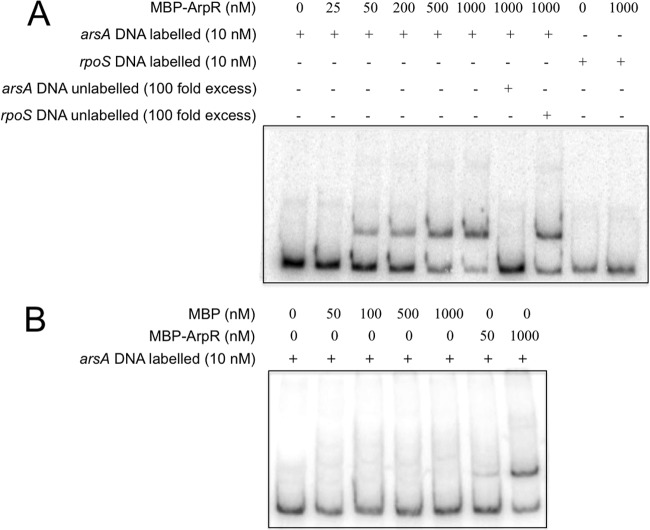
ArpR specifically binds the regulatory arsA region. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed to analyze ArpR binding to the regulatory region of arsA. (A) Labeled DNA fragments (10 nM) containing the regulatory region of arsA were incubated with increasing concentrations of MBP-ArpR (0 to 1,000 nM). ArpR binding to arsA was further analyzed by competitive EMSA. As a negative control, a fragment containing the regulatory region of rpoS was included in the DNA binding reaction mix. The labeled DNA fragment containing the regulatory region of arsA was mixed with 1,000 nM MBP-ArpR in the presence or absence of a 100-fold excess of unlabeled specific (arsA) or nonspecific (rpoS) competitor. (B) EMSA with MBP as a negative control. The DNA-protein complexes were resolved in a nondenaturing 6% polyacrylamide gel.