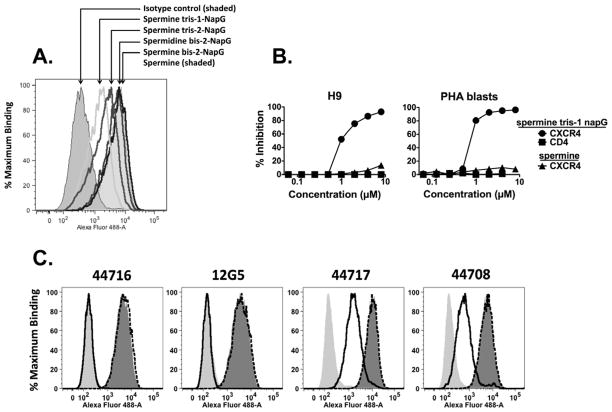
Figure 2. Inhibition of binding of anti-CXCR4 mAbs to cells by naphthylguanide derivitives.
a. H9 lymphoma cells were incubated at 4°C with 1 μM naphthylguanide derivatives in PBS/BSA/azide. After 20 min, anti-CXCR4 mAb 44716 or an isotype control was added to 1 μg/ml. After 1 h at 4°C, the cells were washed and Alexa-fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG was added. Cells were incubated at 4°C for one hour, washed, and fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde. Fluorescence of the cells (10,000 events) was then analyzed by flow cytometry. b. H9 cells or primary T cell blasts were incubated with varying concentrations of spermine tris-1-NapG or spermine alone, and then stained with anti-CXCR4 mAb 12G5 or, as a control, anti-CD4 mAb Sim.2 as described in panel A. c. Inhibition of four different anti-CXCR4 mAbs by 3 μM spermine tris-1-NapG or spermine. Cells were stained as in panel A.