Figure 1. High PKCθ activity in ER-negative breast cancer cell lines increases Fra-1 expression.
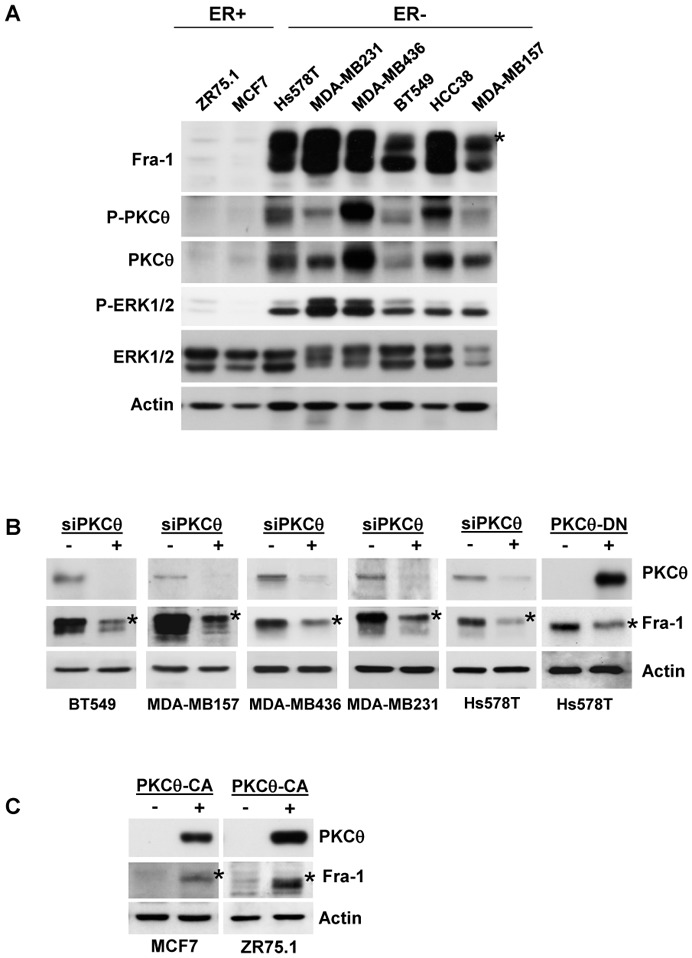
A. Whole-cell extracts (WCEs, 90 μg) from the indicated breast cancer cell lines were analysed using immunoblotting with antibodies against Fra-1, ERK1/2, phospho-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204), PKCθ, phospho-PKCθ (T538) and actin, which was used to confirm equal loading. B. The indicated ER− breast cancer cell lines were transfected with two different siRNAs (3.6 nM each) targeting the PKCθ mRNA. After two successive 48h-transfections, WCEs (90 μg) were subjected to immunoblotting for Fra-1, PKCθ, and actin, the latter being used to confirm equal loading. Alternatively, Hs578T cells were transiently transfected with 2 μg of PKCθ-DN expression vector (+) or empty vector (−) and, 48 h after transfection, WCEs (90 μg) were analysed using immunoblotting. C. The indicated ER+ breast cancer cell lines were transiently transfected with 2 μg of PKCθ-CA expression vector (+) or empty vector (−) and analysed as in B. In A, B and C, phosphorylated Fra-1 forms are indicated by an asterisk.
