Figure 9. LTD regulation by synergistic actions of CaMKII and NO.
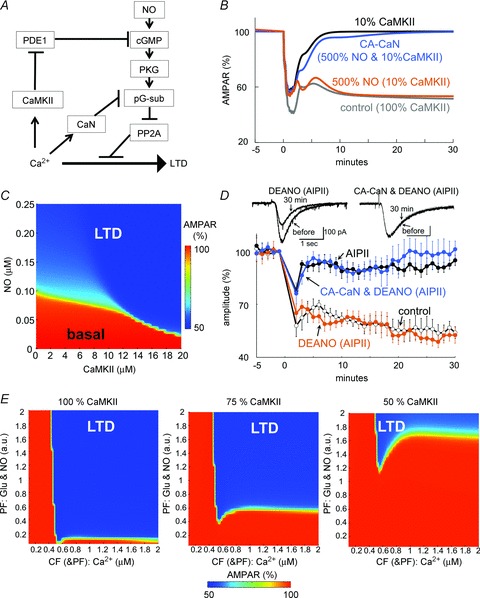
A, signalling scheme for interactions of Ca2+-activated CaMKII and calcineurin, and the NO-mediated activation of cGMP pathway contributing to LTD. B, simulated time courses of non-phosphorylated AMPARs before and after the LTD conditioning with or without CaMKII reduction to 10%, NO increase to 500%, and/or replacement of 10% calcineurin by the constitutively active form (CA-CaN). C, relation of CaMKII amount and basal NO required for LTD establishment. The amount of non-phosphorylated AMPARs 30 min after the conditioning stimulation was plotted in a colour scale as a function of basal NO concentration and CaMKII amount. D, time courses of glutamate response amplitudes before and after the conditioning stimulation in the presence of AIPII and DEANO in a cultured Purkinje cell with or without transfection of CA-CaN. n = 5 for each. Data without (control) and with AIPII (AIPII, same as those in Fig. 2B) are presented for comparison. E, simulated CaMKII-dependent dynamic relation between the intensity of Ca2+ increase primarily reflecting CF inputs and the intensity of glutamate and NO inputs reflecting PF inputs. The amount of non-phosphorylated AMPARs 30 min after the conditioning stimulation with different amounts of CaMKII was plotted in a colour scale against the strengths of PF and CF (& PF) inputs.
