Figure 1. Fasting changes the effects of leptin on gastric vagal afferent mechanosensitivity.
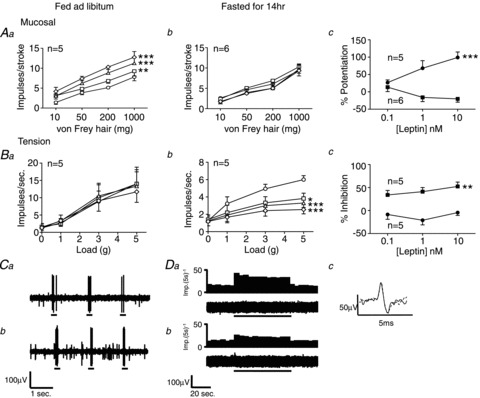
Single fibre recording stimulus–response curves of mucosal (Aa, n= 5; Ab, n= 6) and tension (Ba, n= 5; Bb, n= 5) receptors to mucosal stroking and circular tension, respectively, in fed (Aa and Ba) and fasted mice (Ab and Bb) before ○ and after exposure to leptin 0.1 nm□, 1 nmΔ and 10 nm◊. Ac and Bc, percentage change in response to a 50 mg von Frey hair and 3 g tension, respectively, compared with control at varying concentrations of leptin in fed (•) and fasted (▪) mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control (two-way ANOVA). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. C, original recording, from a fed mouse, of a mucosal receptor response to mucosal stroking with a 50 mg von Frey hair (a) prior to leptin and (b) after addition of leptin (10 nm). D, original recording, from a fasted mouse, of a tension receptor response to 3 g circular tension (a) prior to leptin, (b) after addition of leptin (10 nm), and (c) the average spike shape of the tension receptor prior to leptin (continuous line) and after addition of leptin (dashed line) illustrating that both responses were obtained from the same unit.
