Figure 2. Repeated cocaine exposure does not induce changes in the current–voltage (I–V) relationship of AMPAR-mediated EPSC in hypocretin neurons.
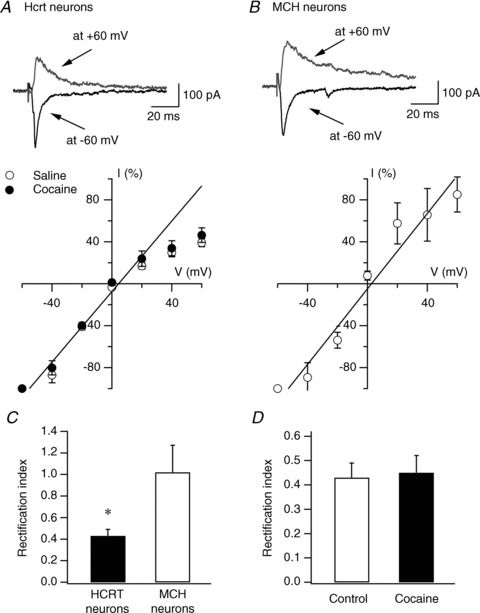
A, I–V relationship of evoked AMPAR-EPSCs recorded in hypocretin (Hcrt) neurons in naive (open circles) and cocaine-treated (filled circles) mice. Representative traces from naive mice are shown on the upper part of the panel. The straight line represents the linear regression of mean EPSC amplitude at negative potentials. B, representative traces (upper) and I–V relationship (lower) of evoked AMPAR-EPSCs recorded in melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)-containing neurons in MCH-GFP mice. The straight line represents the linear regression of mean EPSC amplitude at negative potentials. C, mean RI in hypocretin and MCH neurons is presented. D, mean RI in hypocretin neurons from control and cocaine-treated mice is presented.
