Figure 5. Duration of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity at glutamatergic synapses on hypocretin neurons following cocaine exposure.
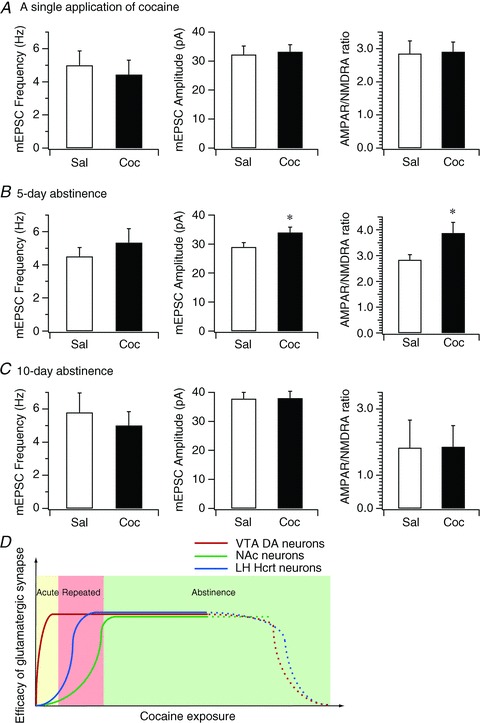
A, bar graph shows the mean frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs and mean AMPAR/NMDAR ratio in hypocretin neurons in control and cocaine-treated mice 1 day after a single exposure to cocaine. B, bar graph shows the mean frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs and mean AMPAR/NMDAR ratio in hypocretin neurons in control and cocaine-treated mice on the 5th day of withdrawal following the 3-day cocaine regimen. *P < 0.05, paired t test. C, bar graph shows the mean frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs and mean AMPAR/NMDAR ratio in hypocretin neurons in control and cocaine-treated mice on the 10th day of withdrawal after the 3-day cocaine regimen. D, the diagram summarizes the time courses of synaptic potentiation in the VTA, NAc and hypocretin neurons induced by exposure to cocaine. Our data suggest that the onset of expression of experience-dependent synaptic potentiation in hypocretin neurons (blue line) is later than synaptic potentiation induced in the VTA (red line) (Ungless et al. 2001) and earlier than in the NAc (green line) (Kourrich et al. 2007), which implicates the distinctive roles of synaptic plasticity in these areas in the development of animal behaviours relevant to cocaine addiction.
